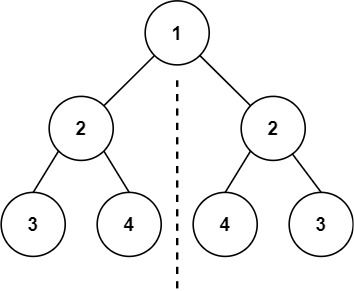
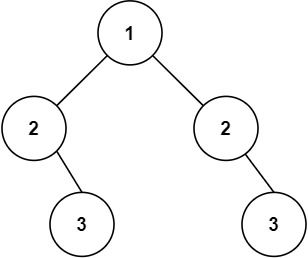
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 输出:false
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
方法一:递归
我们设计一个函数
函数
- 如果
$root1$ 和$root2$ 都为空,则两个二叉树对称,返回true; - 如果
$root1$ 和$root2$ 中只有一个为空,或者$root1.val \neq root2.val$ ,则两个二叉树不对称,返回false; - 否则,判断
$root1$ 的左子树和$root2$ 的右子树是否对称,以及$root1$ 的右子树和$root2$ 的左子树是否对称,这里使用了递归。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
def dfs(root1, root2):
if root1 is None and root2 is None:
return True
if root1 is None or root2 is None or root1.val != root2.val:
return False
return dfs(root1.left, root2.right) and dfs(root1.right, root2.left)
return dfs(root, root)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, root);
}
private boolean dfs(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) {
return true;
}
if (root1 == null || root2 == null || root1.val != root2.val) {
return false;
}
return dfs(root1.left, root2.right) && dfs(root1.right, root2.left);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
function<bool(TreeNode*, TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) -> bool {
if (!root1 && !root2) return true;
if (!root1 || !root2 || root1->val != root2->val) return false;
return dfs(root1->left, root2->right) && dfs(root1->right, root2->left);
};
return dfs(root, root);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
var dfs func(*TreeNode, *TreeNode) bool
dfs = func(root1, root2 *TreeNode) bool {
if root1 == nil && root2 == nil {
return true
}
if root1 == nil || root2 == nil || root1.Val != root2.Val {
return false
}
return dfs(root1.Left, root2.Right) && dfs(root1.Right, root2.Left)
}
return dfs(root, root)
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
const dfs = (root1: TreeNode | null, root2: TreeNode | null) => {
if (root1 == root2) {
return true;
}
if (root1 == null || root2 == null || root1.val != root2.val) {
return false;
}
return dfs(root1.left, root2.right) && dfs(root1.right, root2.left);
};
function isSymmetric(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
return dfs(root.left, root.right);
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(root1: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, root2: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
if root1.is_none() && root2.is_none() {
return true;
}
if root1.is_none() || root2.is_none() {
return false;
}
let node1 = root1.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
let node2 = root2.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
node1.val == node2.val
&& Self::dfs(&node1.left, &node2.right)
&& Self::dfs(&node1.right, &node2.left)
}
pub fn is_symmetric(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
Self::dfs(&node.left, &node.right)
}
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn is_symmetric(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
let root = root.unwrap();
let mut node = root.as_ref().borrow_mut();
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
queue.push_back([node.left.take(), node.right.take()]);
while let Some([root1, root2]) = queue.pop_front() {
if root1.is_none() && root2.is_none() {
continue;
}
if root1.is_none() || root2.is_none() {
return false;
}
if let (Some(node1), Some(node2)) = (root1, root2) {
let mut node1 = node1.as_ref().borrow_mut();
let mut node2 = node2.as_ref().borrow_mut();
if node1.val != node2.val {
return false;
}
queue.push_back([node1.left.take(), node2.right.take()]);
queue.push_back([node1.right.take(), node2.left.take()]);
}
}
true
}
}