When the calibration_mode is set to 1 in the fximu_params.yaml file, the unit outputs raw sensor values at /imu/raw topic.
The complementary filter is not initialized, and the hard iron and soft iron corrections are not processed, but device is configured according to sensor_read_rate, output_rate_divider, gfsr, and afsron the yaml file.
Notice: sudo apt install socat
-
Set
calibration_modeto 1, and selectsensor_read_rate100hz andoutput_rate_dividerto 2 setting output rate to 50hz, in the fximu_params.yaml file. -
Run
roslaunch fximu fx.launchto launch rosserial. -
Run
rostopic echo /imu/rawto verify raw data is being published, and device is in calibration mode. -
Run
socat.shprovided in scripts directory. This will create/dev/ttyCAL0and/dev/ttyCAL1virtual ports. -
Run
perms.shprovided in the scripts directory. This will fix the permissions of newly created devices. -
Run
cal_bridge.pyprogram provided in the scripts directory. This python program will read data from/imu/rawtopic, and then send those values to/dev/ttyCAL0, which will be forwarded to/dev/ttyCAL1by socat, as plaintext raw values. -
Verify that the calibration system is running:
screen /dev/ttyCAL1 115200you should see values running as:
Raw:-73,2054,120,22,-17,51,232,631,277
To quit screen press CTRL-A and \ keys.
Raw sensor data is output as an array of 9, as explained below:
data[0] = accelRD.x;
data[1] = accelRD.y;
data[2] = accelRD.z;
data[3] = gyroRD.x;
data[4] = gyroRD.y;
data[5] = gyroRD.z;
data[6] = magRD.x;
data[7] = magRD.y;
data[8] = magRD.z;
If you are making the calibration on robot, Steps 1, 2, 3 should be done in the robot, while the 4,5,6,7 should pe performed on the host.
To Perform the actual calibration: Download and compile https://github.com/altineller/MotionCal. This is a slightly modified version of the https://github.com/PaulStoffregen/MotionCal. The portslist.cpp file has been modified so it can see our pseudo terminal /dev/ttyCAL1 port.
The prerequisites for compiling the program under ubuntu 20.04 are explained at https://github.com/altineller/MotionCal/blob/master/README.md
Compile the program by issuing make. If you have problems building MotionCal program, see: https://forum.pjrc.com/threads/57378-Cannot-make-MotionCal-for-Linux
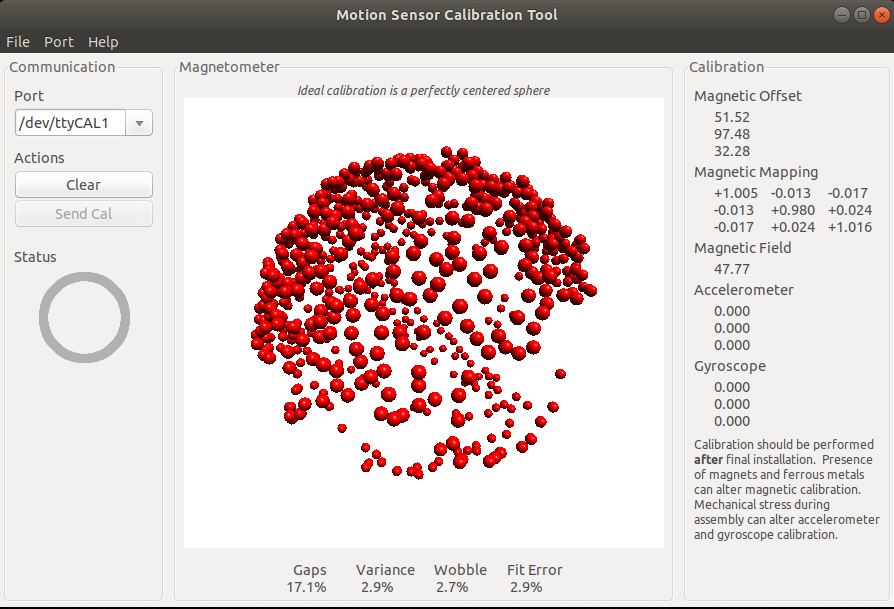
You should turn the sensor until you see see red dots arranged as a sphere like in the picture below:
Rotate the sensor in all directions until gaps are less than 1% and variance less than 2%. At this state you can get a screenshot of calibration screen, and put those values in the hard and soft iron correction matrices defined in fximu_params.yaml file.
Licenses
 |
 |
|---|