| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
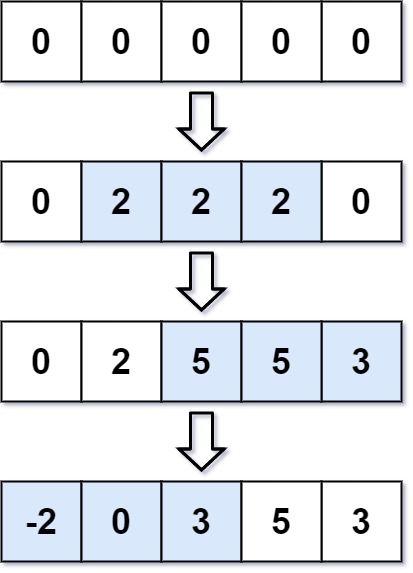
You are given an integer length and an array updates where updates[i] = [startIdxi, endIdxi, inci].
You have an array arr of length length with all zeros, and you have some operation to apply on arr. In the ith operation, you should increment all the elements arr[startIdxi], arr[startIdxi + 1], ..., arr[endIdxi] by inci.
Return arr after applying all the updates.
Example 1:
Input: length = 5, updates = [[1,3,2],[2,4,3],[0,2,-2]] Output: [-2,0,3,5,3]
Example 2:
Input: length = 10, updates = [[2,4,6],[5,6,8],[1,9,-4]] Output: [0,-4,2,2,2,4,4,-4,-4,-4]
Constraints:
1 <= length <= 1050 <= updates.length <= 1040 <= startIdxi <= endIdxi < length-1000 <= inci <= 1000
This is a template problem for difference arrays.
We define
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def getModifiedArray(self, length: int, updates: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
d = [0] * length
for l, r, c in updates:
d[l] += c
if r + 1 < length:
d[r + 1] -= c
return list(accumulate(d))class Solution {
public int[] getModifiedArray(int length, int[][] updates) {
int[] d = new int[length];
for (var e : updates) {
int l = e[0], r = e[1], c = e[2];
d[l] += c;
if (r + 1 < length) {
d[r + 1] -= c;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
d[i] += d[i - 1];
}
return d;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getModifiedArray(int length, vector<vector<int>>& updates) {
vector<int> d(length);
for (const auto& e : updates) {
int l = e[0], r = e[1], c = e[2];
d[l] += c;
if (r + 1 < length) {
d[r + 1] -= c;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
d[i] += d[i - 1];
}
return d;
}
};func getModifiedArray(length int, updates [][]int) []int {
d := make([]int, length)
for _, e := range updates {
l, r, c := e[0], e[1], e[2]
d[l] += c
if r+1 < length {
d[r+1] -= c
}
}
for i := 1; i < length; i++ {
d[i] += d[i-1]
}
return d
}function getModifiedArray(length: number, updates: number[][]): number[] {
const d: number[] = Array(length).fill(0);
for (const [l, r, c] of updates) {
d[l] += c;
if (r + 1 < length) {
d[r + 1] -= c;
}
}
for (let i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
d[i] += d[i - 1];
}
return d;
}/**
* @param {number} length
* @param {number[][]} updates
* @return {number[]}
*/
var getModifiedArray = function (length, updates) {
const d = Array(length).fill(0);
for (const [l, r, c] of updates) {
d[l] += c;
if (r + 1 < length) {
d[r + 1] -= c;
}
}
for (let i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
d[i] += d[i - 1];
}
return d;
};The time complexity is
A Binary Indexed Tree (BIT), also known as a Fenwick Tree, can efficiently perform the following two operations:
-
Point Update
update(x, delta): Add a value$delta$ to the number at position$x$ in the sequence. -
Prefix Sum Query
query(x): Query the sum of the interval$[1, ... , x]$ in the sequence, i.e., the prefix sum up to position$x$ .
The time complexity for both operations is
class BinaryIndexedTree:
__slots__ = "n", "c"
def __init__(self, n: int):
self.n = n
self.c = [0] * (n + 1)
def update(self, x: int, delta: int) -> None:
while x <= self.n:
self.c[x] += delta
x += x & -x
def query(self, x: int) -> int:
s = 0
while x:
s += self.c[x]
x -= x & -x
return s
class Solution:
def getModifiedArray(self, length: int, updates: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
tree = BinaryIndexedTree(length)
for l, r, c in updates:
tree.update(l + 1, c)
tree.update(r + 2, -c)
return [tree.query(i + 1) for i in range(length)]l
class BinaryIndexedTree {
private int n;
private int[] c;
public BinaryIndexedTree(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.c = new int[n + 1];
}
public void update(int x, int delta) {
for (; x <= n; x += x & -x) {
c[x] += delta;
}
}
public int query(int x) {
int s = 0;
for (; x > 0; x -= x & -x) {
s += c[x];
}
return s;
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] getModifiedArray(int length, int[][] updates) {
var tree = new BinaryIndexedTree(length);
for (var e : updates) {
int l = e[0], r = e[1], c = e[2];
tree.update(l + 1, c);
tree.update(r + 2, -c);
}
int[] ans = new int[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
ans[i] = tree.query(i + 1);
}
return ans;
}
}class BinaryIndexedTree {
private:
int n;
vector<int> c;
public:
BinaryIndexedTree(int n)
: n(n)
, c(n + 1) {}
void update(int x, int delta) {
for (; x <= n; x += x & -x) {
c[x] += delta;
}
}
int query(int x) {
int s = 0;
for (; x > 0; x -= x & -x) {
s += c[x];
}
return s;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getModifiedArray(int length, vector<vector<int>>& updates) {
BinaryIndexedTree* tree = new BinaryIndexedTree(length);
for (const auto& e : updates) {
int l = e[0], r = e[1], c = e[2];
tree->update(l + 1, c);
tree->update(r + 2, -c);
}
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
ans.push_back(tree->query(i + 1));
}
return ans;
}
};type BinaryIndexedTree struct {
n int
c []int
}
func NewBinaryIndexedTree(n int) *BinaryIndexedTree {
return &BinaryIndexedTree{n: n, c: make([]int, n+1)}
}
func (bit *BinaryIndexedTree) update(x, delta int) {
for ; x <= bit.n; x += x & -x {
bit.c[x] += delta
}
}
func (bit *BinaryIndexedTree) query(x int) int {
s := 0
for ; x > 0; x -= x & -x {
s += bit.c[x]
}
return s
}
func getModifiedArray(length int, updates [][]int) (ans []int) {
bit := NewBinaryIndexedTree(length)
for _, e := range updates {
l, r, c := e[0], e[1], e[2]
bit.update(l+1, c)
bit.update(r+2, -c)
}
for i := 1; i <= length; i++ {
ans = append(ans, bit.query(i))
}
return
}class BinaryIndexedTree {
private n: number;
private c: number[];
constructor(n: number) {
this.n = n;
this.c = Array(n + 1).fill(0);
}
update(x: number, delta: number): void {
for (; x <= this.n; x += x & -x) {
this.c[x] += delta;
}
}
query(x: number): number {
let s = 0;
for (; x > 0; x -= x & -x) {
s += this.c[x];
}
return s;
}
}
function getModifiedArray(length: number, updates: number[][]): number[] {
const bit = new BinaryIndexedTree(length);
for (const [l, r, c] of updates) {
bit.update(l + 1, c);
bit.update(r + 2, -c);
}
return Array.from({ length }, (_, i) => bit.query(i + 1));
}/**
* @param {number} length
* @param {number[][]} updates
* @return {number[]}
*/
var getModifiedArray = function (length, updates) {
class BinaryIndexedTree {
constructor(n) {
this.n = n;
this.c = Array(n + 1).fill(0);
}
update(x, delta) {
while (x <= this.n) {
this.c[x] += delta;
x += x & -x;
}
}
query(x) {
let s = 0;
while (x > 0) {
s += this.c[x];
x -= x & -x;
}
return s;
}
}
const bit = new BinaryIndexedTree(length);
for (const [l, r, c] of updates) {
bit.update(l + 1, c);
bit.update(r + 2, -c);
}
return Array.from({ length }, (_, i) => bit.query(i + 1));
};