| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
困难 |
|
设计一个算法,可以将 N 叉树编码为二叉树,并能将该二叉树解码为原 N 叉树。一个 N 叉树是指每个节点都有不超过 N 个孩子节点的有根树。类似地,一个二叉树是指每个节点都有不超过 2 个孩子节点的有根树。你的编码 / 解码的算法的实现没有限制,你只需要保证一个 N 叉树可以编码为二叉树且该二叉树可以解码回原始 N 叉树即可。
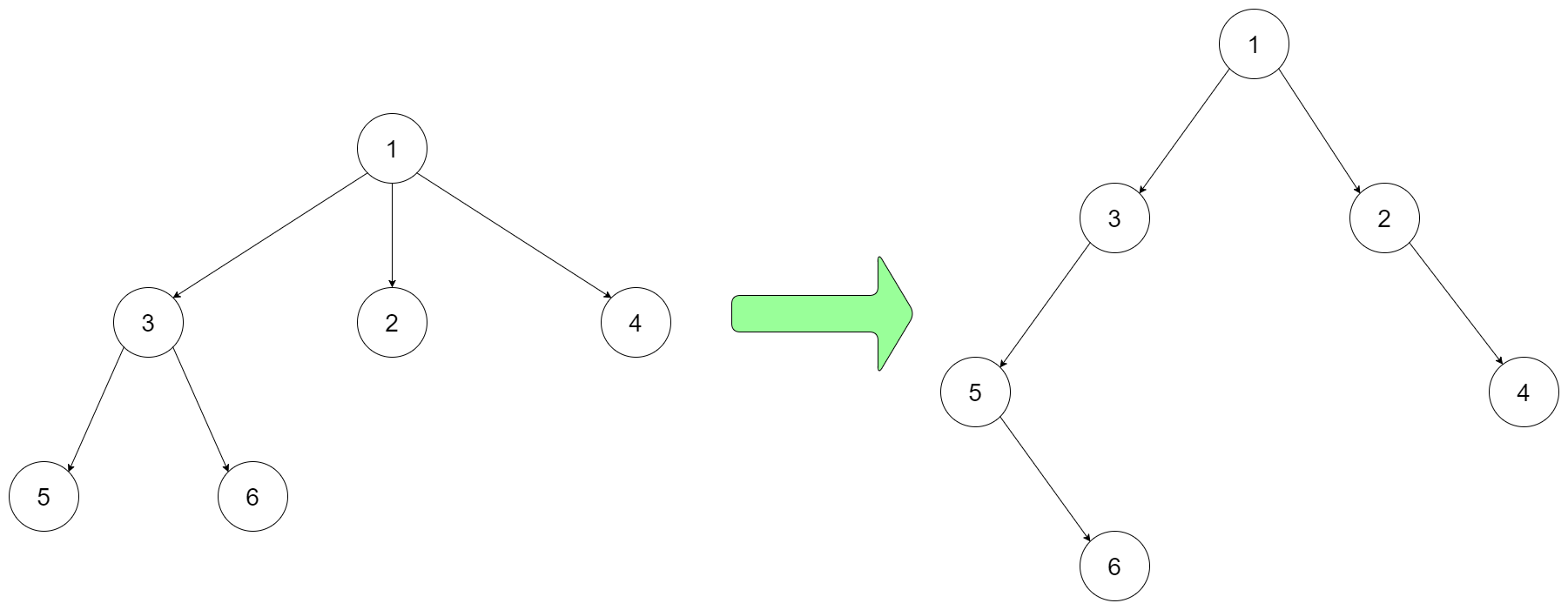
例如,你可以将下面的 3-叉 树以该种方式编码:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
注意,上面的方法仅仅是一个例子,可能可行也可能不可行。你没有必要遵循这种形式转化,你可以自己创造和实现不同的方法。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] 输出:[1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] 输出:[1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
N的范围在[1, 104]0 <= Node.val <= 104- N 叉树的高度小于等于
1000。 - 不要使用类成员 / 全局变量 / 静态变量来存储状态。你的编码和解码算法应是无状态的。
我们可以将二叉树的左指针指向 N 叉树的第一个孩子,将二叉树的右指针指向 N 叉树的下一个兄弟节点。
时间复杂度
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: Optional[int] = None, children: Optional[List['Node']] = None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
"""
class Codec:
# Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
def encode(self, root: "Optional[Node]") -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
return None
node = TreeNode(root.val)
if not root.children:
return node
left = self.encode(root.children[0])
node.left = left
for child in root.children[1:]:
left.right = self.encode(child)
left = left.right
return node
# Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
def decode(self, data: Optional[TreeNode]) -> "Optional[Node]":
if data is None:
return None
node = Node(data.val, [])
if data.left is None:
return node
left = data.left
while left:
node.children.append(self.decode(left))
left = left.right
return node
# Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
# codec = Codec()
# codec.decode(codec.encode(root))/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Codec {
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
public TreeNode encode(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(root.val);
if (root.children == null || root.children.isEmpty()) {
return node;
}
TreeNode left = encode(root.children.get(0));
node.left = left;
for (int i = 1; i < root.children.size(); i++) {
left.right = encode(root.children.get(i));
left = left.right;
}
return node;
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
public Node decode(TreeNode data) {
if (data == null) {
return null;
}
Node node = new Node(data.val, new ArrayList<>());
if (data.left == null) {
return node;
}
TreeNode left = data.left;
while (left != null) {
node.children.add(decode(left));
left = left.right;
}
return node;
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec = new Codec();
// codec.decode(codec.encode(root));/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
TreeNode* encode(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(root->val);
if (root->children.empty()) {
return node;
}
TreeNode* left = encode(root->children[0]);
node->left = left;
for (int i = 1; i < root->children.size(); i++) {
left->right = encode(root->children[i]);
left = left->right;
}
return node;
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
Node* decode(TreeNode* data) {
if (data == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
Node* node = new Node(data->val, vector<Node*>());
if (data->left == nullptr) {
return node;
}
TreeNode* left = data->left;
while (left != nullptr) {
node->children.push_back(decode(left));
left = left->right;
}
return node;
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec;
// codec.decode(codec.encode(root));/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
type Codec struct {
}
func Constructor() *Codec {
return &Codec{}
}
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
func (this *Codec) encode(root *Node) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
node := &TreeNode{Val: root.Val}
if len(root.Children) == 0 {
return node
}
left := this.encode(root.Children[0])
node.Left = left
for i := 1; i < len(root.Children); i++ {
left.Right = this.encode(root.Children[i])
left = left.Right
}
return node
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
func (this *Codec) decode(data *TreeNode) *Node {
if data == nil {
return nil
}
node := &Node{Val: data.Val, Children: []*Node{}}
if data.Left == nil {
return node
}
left := data.Left
for left != nil {
node.Children = append(node.Children, this.decode(left))
left = left.Right
}
return node
}
/**
* Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor();
* bst := obj.encode(root);
* ans := obj.decode(bst);
*//**
* Definition for _Node.
* class _Node {
* val: number
* children: _Node[]
*
* constructor(v: number) {
* this.val = v;
* this.children = [];
* }
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
class Codec {
constructor() {}
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
serialize(root: _Node | null): TreeNode | null {
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
const node = new TreeNode(root.val);
if (root.children.length === 0) {
return node;
}
let left: TreeNode | null = this.serialize(root.children[0]);
node.left = left;
for (let i = 1; i < root.children.length; i++) {
if (left) {
left.right = this.serialize(root.children[i]);
left = left.right;
}
}
return node;
}
// Decodes your binary tree back to an n-ary tree.
deserialize(root: TreeNode | null): _Node | null {
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
const node = new _Node(root.val);
if (root.left === null) {
return node;
}
let left: TreeNode | null = root.left;
while (left !== null) {
node.children.push(this.deserialize(left));
left = left.right;
}
return node;
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec = new Codec();
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));