| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
示例1:
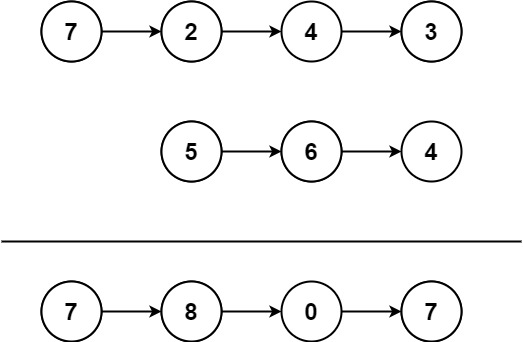
输入:l1 = [7,2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,8,0,7]
示例2:
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[8,0,7]
示例3:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
提示:
- 链表的长度范围为
[1, 100] 0 <= node.val <= 9- 输入数据保证链表代表的数字无前导 0
进阶:如果输入链表不能翻转该如何解决?
手动翻转链表 l1 与 l2,将此题转换为 2. 两数相加,相加过程一致。对于最后返回的结果链表也需要进行翻转,共计三次。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(
self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]
) -> Optional[ListNode]:
s1, s2 = [], []
while l1:
s1.append(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
while l2:
s2.append(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
dummy = ListNode()
carry = 0
while s1 or s2 or carry:
s = (0 if not s1 else s1.pop()) + (0 if not s2 else s2.pop()) + carry
carry, val = divmod(s, 10)
# node = ListNode(val, dummy.next)
# dummy.next = node
dummy.next = ListNode(val, dummy.next)
return dummy.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Deque<Integer> s1 = new ArrayDeque<>();
Deque<Integer> s2 = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (; l1 != null; l1 = l1.next) {
s1.push(l1.val);
}
for (; l2 != null; l2 = l2.next) {
s2.push(l2.val);
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
int carry = 0;
while (!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty() || carry != 0) {
int s = (s1.isEmpty() ? 0 : s1.pop()) + (s2.isEmpty() ? 0 : s2.pop()) + carry;
// ListNode node = new ListNode(s % 10, dummy.next);
// dummy.next = node;
dummy.next = new ListNode(s % 10, dummy.next);
carry = s / 10;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
stack<int> s1;
stack<int> s2;
for (; l1; l1 = l1->next) s1.push(l1->val);
for (; l2; l2 = l2->next) s2.push(l2->val);
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode();
int carry = 0;
while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty() || carry) {
int s = carry;
if (!s1.empty()) {
s += s1.top();
s1.pop();
}
if (!s2.empty()) {
s += s2.top();
s2.pop();
}
// ListNode* node = new ListNode(s % 10, dummy->next);
// dummy->next = node;
dummy->next = new ListNode(s % 10, dummy->next);
carry = s / 10;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
s1, s2 := arraystack.New(), arraystack.New()
for l1 != nil {
s1.Push(l1.Val)
l1 = l1.Next
}
for l2 != nil {
s2.Push(l2.Val)
l2 = l2.Next
}
carry, dummy := 0, new(ListNode)
for !s1.Empty() || !s2.Empty() || carry > 0 {
s := carry
v, ok := s1.Pop()
if ok {
s += v.(int)
}
v, ok = s2.Pop()
if ok {
s += v.(int)
}
// node := &ListNode{s % 10, dummy.Next}
// dummy.Next = node
dummy.Next = &ListNode{s % 10, dummy.Next}
carry = s / 10
}
return dummy.Next
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function addTwoNumbers(l1: ListNode | null, l2: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
const s1: number[] = [];
const s2: number[] = [];
for (; l1; l1 = l1.next) {
s1.push(l1.val);
}
for (; l2; l2 = l2.next) {
s2.push(l2.val);
}
const dummy = new ListNode();
let carry = 0;
while (s1.length || s2.length || carry) {
const s = (s1.pop() ?? 0) + (s2.pop() ?? 0) + carry;
// const node = new ListNode(s % 10, dummy.next);
// dummy.next = node;
dummy.next = new ListNode(s % 10, dummy.next);
carry = Math.floor(s / 10);
}
return dummy.next;
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
fn reverse(mut head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut pre = None;
while let Some(mut node) = head {
let next = node.next.take();
node.next = pre.take();
pre = Some(node);
head = next;
}
pre
}
pub fn add_two_numbers(
mut l1: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
mut l2: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
l1 = Self::reverse(l1);
l2 = Self::reverse(l2);
let mut dummy = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(0)));
let mut cur = &mut dummy;
let mut sum = 0;
while l1.is_some() || l2.is_some() || sum != 0 {
if let Some(node) = l1 {
sum += node.val;
l1 = node.next;
}
if let Some(node) = l2 {
sum += node.val;
l2 = node.next;
}
cur.as_mut().unwrap().next = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(sum % 10)));
cur = &mut cur.as_mut().unwrap().next;
sum /= 10;
}
Self::reverse(dummy.unwrap().next.take())
}
}我们可以使用两个栈
遍历时,我们弹出对应栈的栈顶元素,计算它们与进位
最后我们返回答案链表的头节点即可。
时间复杂度
// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
fn create_stack(mut head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut res = vec![];
while let Some(node) = head {
res.push(node.val);
head = node.next;
}
res
}
pub fn add_two_numbers(
l1: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
l2: Option<Box<ListNode>>,
) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut s1 = Self::create_stack(l1);
let mut s2 = Self::create_stack(l2);
let mut dummy = Box::new(ListNode::new(0));
let mut carry = 0;
while !s1.is_empty() || !s2.is_empty() || carry != 0 {
if let Some(val) = s1.pop() {
carry += val;
}
if let Some(val) = s2.pop() {
carry += val;
}
dummy.next = Some(Box::new(ListNode {
val: carry % 10,
next: dummy.next.take(),
}));
carry /= 10;
}
dummy.next.take()
}
}