| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
In this problem, a tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles.
You are given a graph that started as a tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n, with one additional edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from 1 to n, and was not an edge that already existed. The graph is represented as an array edges of length n where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a tree of n nodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the input.
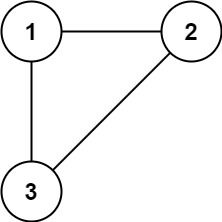
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]] Output: [2,3]
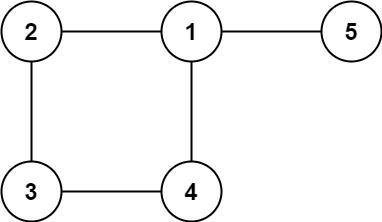
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]] Output: [1,4]
Constraints:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ai < bi <= edges.lengthai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
- The given graph is connected.
According to the problem description, we need to find an edge that can be removed so that the remaining part is a tree with
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def findRedundantConnection(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
def find(x: int) -> int:
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
p = list(range(len(edges)))
for a, b in edges:
pa, pb = find(a - 1), find(b - 1)
if pa == pb:
return [a, b]
p[pa] = pbclass Solution {
private int[] p;
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length;
p = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0;; ++i) {
int pa = find(edges[i][0] - 1);
int pb = find(edges[i][1] - 1);
if (pa == pb) {
return edges[i];
}
p[pa] = pb;
}
}
private int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = edges.size();
vector<int> p(n);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
function<int(int)> find = [&](int x) {
return x == p[x] ? x : p[x] = find(p[x]);
};
for (int i = 0;; ++i) {
int pa = find(edges[i][0] - 1);
int pb = find(edges[i][1] - 1);
if (pa == pb) {
return edges[i];
}
p[pa] = pb;
}
}
};func findRedundantConnection(edges [][]int) []int {
n := len(edges)
p := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
}
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
for i := 0; ; i++ {
pa, pb := find(edges[i][0]-1), find(edges[i][1]-1)
if pa == pb {
return edges[i]
}
p[pa] = pb
}
}function findRedundantConnection(edges: number[][]): number[] {
const n = edges.length;
const p: number[] = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
const find = (x: number): number => {
if (p[x] !== x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
for (let i = 0; ; ++i) {
const pa = find(edges[i][0] - 1);
const pb = find(edges[i][1] - 1);
if (pa === pb) {
return edges[i];
}
p[pa] = pb;
}
}/**
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findRedundantConnection = function (edges) {
const n = edges.length;
const p = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
const find = x => {
if (p[x] !== x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
for (let i = 0; ; ++i) {
const pa = find(edges[i][0] - 1);
const pb = find(edges[i][1] - 1);
if (pa === pb) {
return edges[i];
}
p[pa] = pb;
}
};Here is a template approach using Union-Find for your reference.
The time complexity is
class UnionFind:
__slots__ = "p", "size"
def __init__(self, n: int):
self.p: List[int] = list(range(n))
self.size: List[int] = [1] * n
def find(self, x: int) -> int:
if self.p[x] != x:
self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x])
return self.p[x]
def union(self, a: int, b: int) -> bool:
pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b)
if pa == pb:
return False
if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]:
self.p[pb] = pa
self.size[pa] += self.size[pb]
else:
self.p[pa] = pb
self.size[pb] += self.size[pa]
return True
class Solution:
def findRedundantConnection(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
uf = UnionFind(len(edges))
for a, b in edges:
if not uf.union(a - 1, b - 1):
return [a, b]class UnionFind {
private final int[] p;
private final int[] size;
public UnionFind(int n) {
p = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
public boolean union(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
}
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
return true;
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(edges.length);
for (int i = 0;; ++i) {
if (!uf.union(edges[i][0] - 1, edges[i][1] - 1)) {
return edges[i];
}
}
}
}class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(int n) {
p = vector<int>(n);
size = vector<int>(n, 1);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
}
bool unite(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
}
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
return true;
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
private:
vector<int> p, size;
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
UnionFind uf(edges.size());
for (int i = 0;; ++i) {
if (!uf.unite(edges[i][0] - 1, edges[i][1] - 1)) {
return edges[i];
}
}
}
};type unionFind struct {
p, size []int
}
func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind {
p := make([]int, n)
size := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
size[i] = 1
}
return &unionFind{p, size}
}
func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int {
if uf.p[x] != x {
uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x])
}
return uf.p[x]
}
func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool {
pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b)
if pa == pb {
return false
}
if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] {
uf.p[pb] = pa
uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb]
} else {
uf.p[pa] = pb
uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa]
}
return true
}
func findRedundantConnection(edges [][]int) []int {
uf := newUnionFind(len(edges))
for i := 0; ; i++ {
if !uf.union(edges[i][0]-1, edges[i][1]-1) {
return edges[i]
}
}
}class UnionFind {
p: number[];
size: number[];
constructor(n: number) {
this.p = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
this.size = Array(n).fill(1);
}
find(x: number): number {
if (this.p[x] !== x) {
this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]);
}
return this.p[x];
}
union(a: number, b: number): boolean {
const [pa, pb] = [this.find(a), this.find(b)];
if (pa === pb) {
return false;
}
if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) {
this.p[pb] = pa;
this.size[pa] += this.size[pb];
} else {
this.p[pa] = pb;
this.size[pb] += this.size[pa];
}
return true;
}
}
function findRedundantConnection(edges: number[][]): number[] {
const uf = new UnionFind(edges.length);
for (let i = 0; ; ++i) {
if (!uf.union(edges[i][0] - 1, edges[i][1] - 1)) {
return edges[i];
}
}
}class UnionFind {
constructor(n) {
this.p = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
this.size = Array(n).fill(1);
}
find(x) {
if (this.p[x] !== x) {
this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]);
}
return this.p[x];
}
union(a, b) {
const pa = this.find(a);
const pb = this.find(b);
if (pa === pb) {
return false;
}
if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) {
this.p[pb] = pa;
this.size[pa] += this.size[pb];
} else {
this.p[pa] = pb;
this.size[pb] += this.size[pa];
}
return true;
}
}
/**
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findRedundantConnection = function (edges) {
const uf = new UnionFind(edges.length);
for (let i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
if (!uf.union(edges[i][0] - 1, edges[i][1] - 1)) {
return edges[i];
}
}
};