| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
最大树 定义:一棵树,并满足:其中每个节点的值都大于其子树中的任何其他值。
给你最大树的根节点 root 和一个整数 val 。
就像 之前的问题 那样,给定的树是利用 Construct(a) 例程从列表 a(root = Construct(a))递归地构建的:
- 如果
a为空,返回null。 - 否则,令
a[i]作为a的最大元素。创建一个值为a[i]的根节点root。 root的左子树将被构建为Construct([a[0], a[1], ..., a[i - 1]])。root的右子树将被构建为Construct([a[i + 1], a[i + 2], ..., a[a.length - 1]])。- 返回
root。
请注意,题目没有直接给出 a ,只是给出一个根节点 root = Construct(a) 。
假设 b 是 a 的副本,并在末尾附加值 val。题目数据保证 b 中的值互不相同。
返回 Construct(b) 。
示例 1:
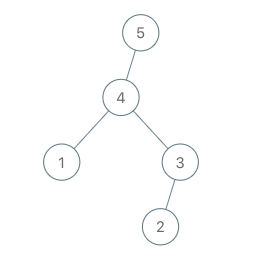
输入:root = [4,1,3,null,null,2], val = 5 输出:[5,4,null,1,3,null,null,2] 解释:a = [1,4,2,3], b = [1,4,2,3,5]
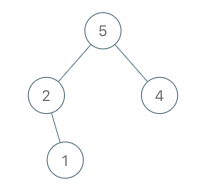
输入:root = [5,2,4,null,1], val = 3 输出:[5,2,4,null,1,null,3] 解释:a = [2,1,5,4], b = [2,1,5,4,3]
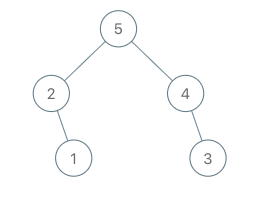
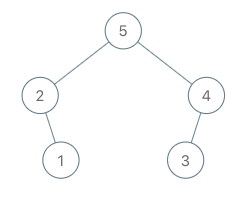
输入:root = [5,2,3,null,1], val = 4 输出:[5,2,4,null,1,3] 解释:a = [2,1,5,3], b = [2,1,5,3,4]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 100]内 1 <= Node.val <= 100- 树中的所有值 互不相同
1 <= val <= 100
如果
如果
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def insertIntoMaxTree(
self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int
) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None or root.val < val:
return TreeNode(val, root)
root.right = self.insertIntoMaxTree(root.right, val)
return root/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoMaxTree(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null || root.val < val) {
return new TreeNode(val, root, null);
}
root.right = insertIntoMaxTree(root.right, val);
return root;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoMaxTree(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (!root || root->val < val) return new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
root->right = insertIntoMaxTree(root->right, val);
return root;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func insertIntoMaxTree(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil || root.Val < val {
return &TreeNode{val, root, nil}
}
root.Right = insertIntoMaxTree(root.Right, val)
return root
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function insertIntoMaxTree(root: TreeNode | null, val: number): TreeNode | null {
if (!root || root.val < val) {
return new TreeNode(val, root);
}
root.right = insertIntoMaxTree(root.right, val);
return root;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn insert_into_max_tree(
mut root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
val: i32,
) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if root.is_none() || root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow().val < val {
return Some(Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode {
val,
left: root.take(),
right: None,
})));
}
{
let mut root = root.as_ref().unwrap().as_ref().borrow_mut();
root.right = Self::insert_into_max_tree(root.right.take(), val);
}
root
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* insertIntoMaxTree(struct TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (!root || root->val < val) {
struct TreeNode* res = (struct TreeNode*) malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
res->val = val;
res->left = root;
res->right = NULL;
return res;
}
root->right = insertIntoMaxTree(root->right, val);
return root;
}搜索右子树,找到
最后返回
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def insertIntoMaxTree(
self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int
) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root.val < val:
return TreeNode(val, root)
curr = root
node = TreeNode(val)
while curr.right and curr.right.val > val:
curr = curr.right
node.left = curr.right
curr.right = node
return root/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoMaxTree(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root.val < val) {
return new TreeNode(val, root, null);
}
TreeNode curr = root;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
while (curr.right != null && curr.right.val > val) {
curr = curr.right;
}
node.left = curr.right;
curr.right = node;
return root;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoMaxTree(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (root->val < val) return new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
TreeNode* curr = root;
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(val);
while (curr->right && curr->right->val > val) curr = curr->right;
node->left = curr->right;
curr->right = node;
return root;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func insertIntoMaxTree(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
if root.Val < val {
return &TreeNode{val, root, nil}
}
node := &TreeNode{Val: val}
curr := root
for curr.Right != nil && curr.Right.Val > val {
curr = curr.Right
}
node.Left = curr.Right
curr.Right = node
return root
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function insertIntoMaxTree(root: TreeNode | null, val: number): TreeNode | null {
if (root.val < val) {
return new TreeNode(val, root);
}
const node = new TreeNode(val);
let curr = root;
while (curr.right && curr.right.val > val) {
curr = curr.right;
}
node.left = curr.right;
curr.right = node;
return root;
}