| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
|
You are given an 8 x 8 matrix representing a chessboard. There is exactly one white rook represented by 'R', some number of white bishops 'B', and some number of black pawns 'p'. Empty squares are represented by '.'.
A rook can move any number of squares horizontally or vertically (up, down, left, right) until it reaches another piece or the edge of the board. A rook is attacking a pawn if it can move to the pawn's square in one move.
Note: A rook cannot move through other pieces, such as bishops or pawns. This means a rook cannot attack a pawn if there is another piece blocking the path.
Return the number of pawns the white rook is attacking.
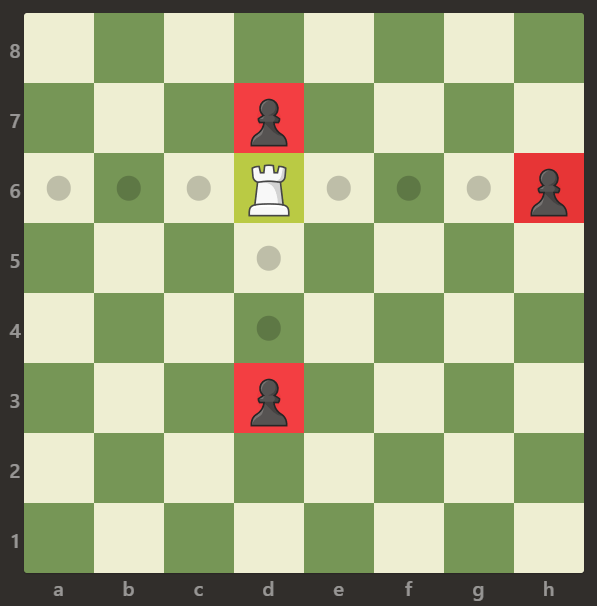
Example 1:
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","R",".",".",".","p"],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
In this example, the rook is attacking all the pawns.
Example 2:
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","B","R","B","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 0
Explanation:
The bishops are blocking the rook from attacking any of the pawns.
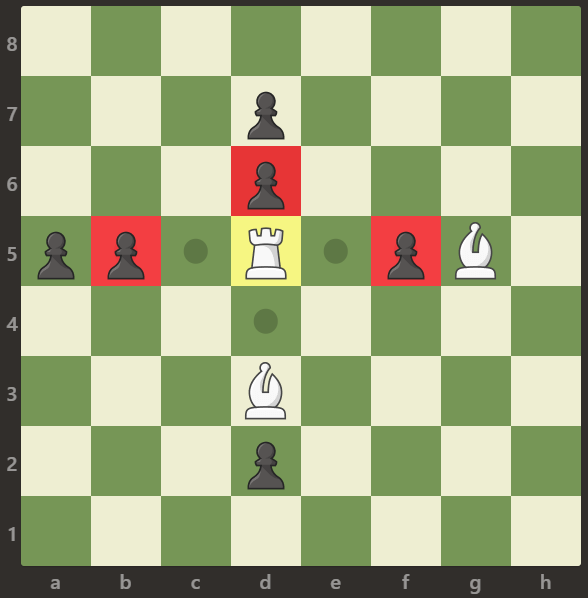
Example 3:
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],["p","p",".","R",".","p","B","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","B",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
The rook is attacking the pawns at positions b5, d6, and f5.
Constraints:
board.length == 8board[i].length == 8board[i][j]is either'R','.','B', or'p'- There is exactly one cell with
board[i][j] == 'R'
We first traverse the board to find the position of the rook
- If it is not the boundary and not a bishop, continue moving forward.
- If it is a pawn, increment the answer by one and stop traversing in that direction.
After traversing in all four directions, we get the answer.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def numRookCaptures(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> int:
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
n = len(board)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if board[i][j] == "R":
ans = 0
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
while 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and board[x][y] != "B":
if board[x][y] == "p":
ans += 1
break
x, y = x + a, y + b
return ansclass Solution {
public int numRookCaptures(char[][] board) {
final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
int n = board.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == 'R') {
int ans = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
while (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] != 'B') {
if (board[x][y] == 'p') {
++ans;
break;
}
x += dirs[k];
y += dirs[k + 1];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numRookCaptures(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
const int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
int n = board.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == 'R') {
int ans = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
while (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] != 'B') {
if (board[x][y] == 'p') {
++ans;
break;
}
x += dirs[k];
y += dirs[k + 1];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};func numRookCaptures(board [][]byte) (ans int) {
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
n := len(board)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if board[i][j] == 'R' {
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k+1]
for x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] != 'B' {
if board[x][y] == 'p' {
ans++
break
}
x += dirs[k]
y += dirs[k+1]
}
}
return
}
}
}
return
}function numRookCaptures(board: string[][]): number {
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
const n = board.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] === 'R') {
let ans = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
let [x, y] = [i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]];
while (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] !== 'B') {
if (board[x][y] === 'p') {
ans++;
break;
}
x += dirs[k];
y += dirs[k + 1];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
}
return 0;
}impl Solution {
pub fn num_rook_captures(board: Vec<Vec<char>>) -> i32 {
let dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
let n = board.len();
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n {
if board[i][j] == 'R' {
let mut ans = 0;
for k in 0..4 {
let mut x = i as i32 + dirs[k];
let mut y = j as i32 + dirs[k + 1];
while x >= 0
&& x < n as i32
&& y >= 0
&& y < n as i32
&& board[x as usize][y as usize] != 'B'
{
if board[x as usize][y as usize] == 'p' {
ans += 1;
break;
}
x += dirs[k];
y += dirs[k + 1];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
}
0
}
}