| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1805 |
第 134 场周赛 Q3 |
|
在两条独立的水平线上按给定的顺序写下 nums1 和 nums2 中的整数。
现在,可以绘制一些连接两个数字 nums1[i] 和 nums2[j] 的直线,这些直线需要同时满足:
-
nums1[i] == nums2[j] - 且绘制的直线不与任何其他连线(非水平线)相交。
请注意,连线即使在端点也不能相交:每个数字只能属于一条连线。
以这种方法绘制线条,并返回可以绘制的最大连线数。
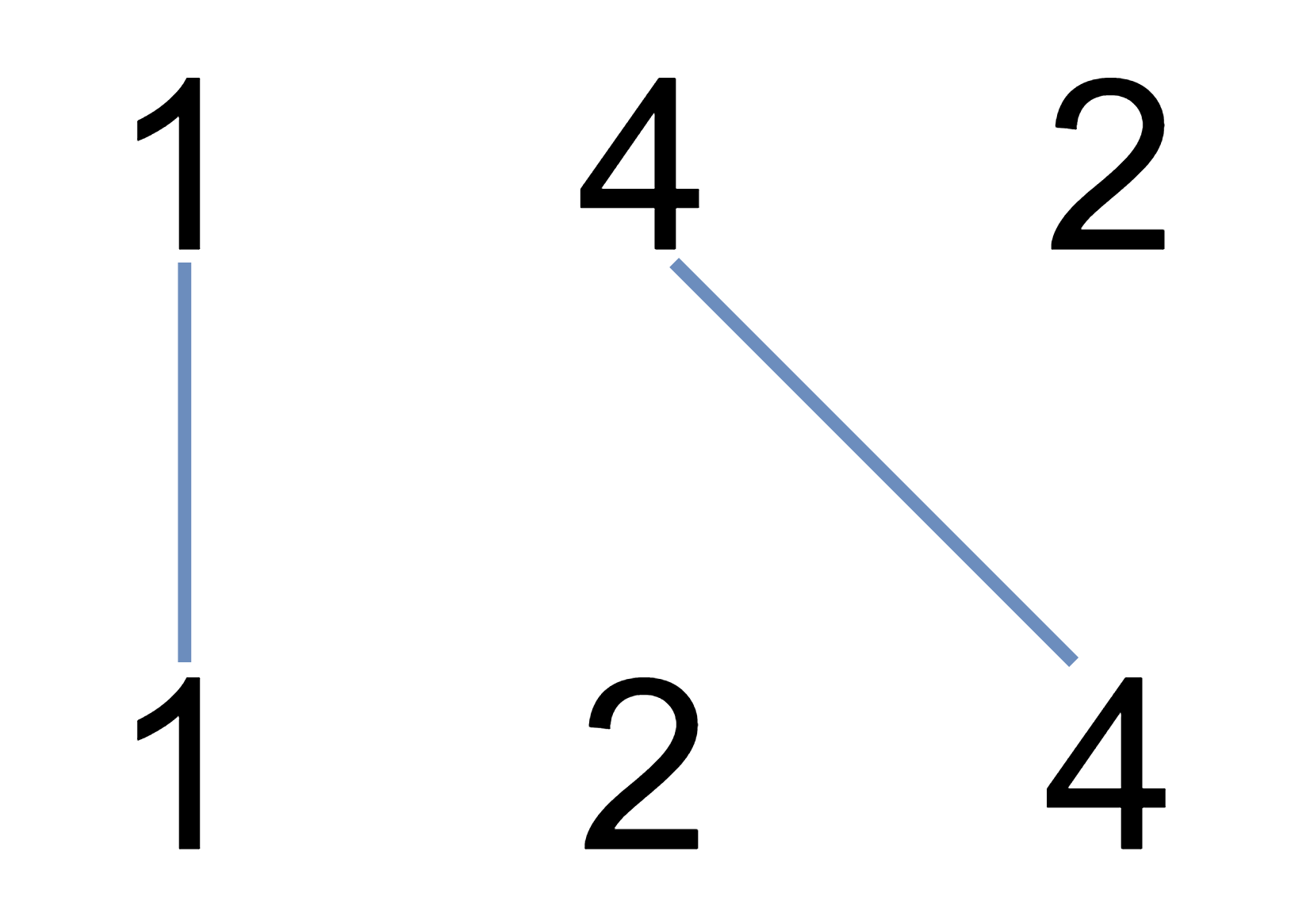
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,4,2], nums2 = [1,2,4] 输出:2 解释:可以画出两条不交叉的线,如上图所示。 但无法画出第三条不相交的直线,因为从 nums1[1]=4 到 nums2[2]=4 的直线将与从 nums1[2]=2 到 nums2[1]=2 的直线相交。
示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [2,5,1,2,5], nums2 = [10,5,2,1,5,2] 输出:3
示例 3:
输入:nums1 = [1,3,7,1,7,5], nums2 = [1,9,2,5,1] 输出:2
提示:
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 5001 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 2000
我们定义
当
当
最后返回
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def maxUncrossedLines(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:
m, n = len(nums1), len(nums2)
f = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
for i, x in enumerate(nums1, 1):
for j, y in enumerate(nums2, 1):
if x == y:
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
else:
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1])
return f[m][n]class Solution {
public int maxUncrossedLines(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int m = nums1.length, n = nums2.length;
int[][] f = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maxUncrossedLines(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int m = nums1.size(), n = nums2.size();
int f[m + 1][n + 1];
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
};func maxUncrossedLines(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) int {
m, n := len(nums1), len(nums2)
f := make([][]int, m+1)
for i := range f {
f[i] = make([]int, n+1)
}
for i := 1; i <= m; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= n; j++ {
if nums1[i-1] == nums2[j-1] {
f[i][j] = f[i-1][j-1] + 1
} else {
f[i][j] = max(f[i-1][j], f[i][j-1])
}
}
}
return f[m][n]
}function maxUncrossedLines(nums1: number[], nums2: number[]): number {
const m = nums1.length;
const n = nums2.length;
const f: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m + 1 }, () => Array(n + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (nums1[i - 1] === nums2[j - 1]) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return f[m][n];
}/**
* @param {number[]} nums1
* @param {number[]} nums2
* @return {number}
*/
var maxUncrossedLines = function (nums1, nums2) {
const m = nums1.length;
const n = nums2.length;
const f = Array.from({ length: m + 1 }, () => Array(n + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (nums1[i - 1] === nums2[j - 1]) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return f[m][n];
};