| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1947 |
Weekly Contest 212 Q3 |
|
You are a hiker preparing for an upcoming hike. You are given heights, a 2D array of size rows x columns, where heights[row][col] represents the height of cell (row, col). You are situated in the top-left cell, (0, 0), and you hope to travel to the bottom-right cell, (rows-1, columns-1) (i.e., 0-indexed). You can move up, down, left, or right, and you wish to find a route that requires the minimum effort.
A route's effort is the maximum absolute difference in heights between two consecutive cells of the route.
Return the minimum effort required to travel from the top-left cell to the bottom-right cell.
Example 1:
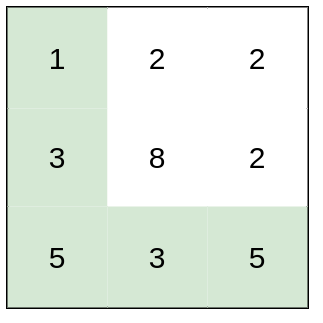
Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] Output: 2 Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells. This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3.
Example 2:
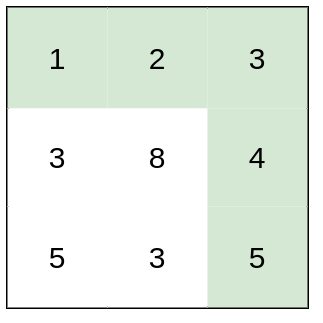
Input: heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: The route of [1,2,3,4,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 1 in consecutive cells, which is better than route [1,3,5,3,5].
Example 3:
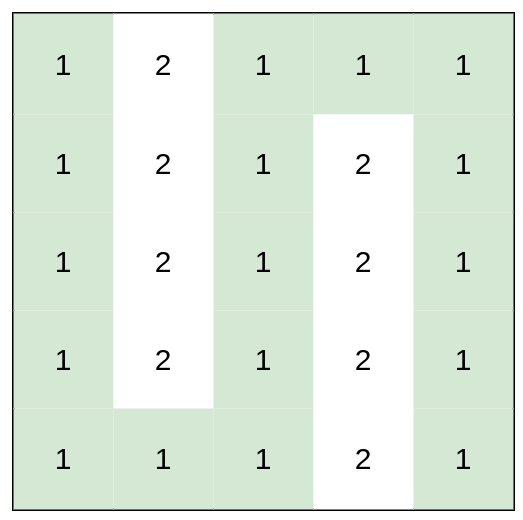
Input: heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] Output: 0 Explanation: This route does not require any effort.
Constraints:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
For this problem, we can treat each cell as a node in a graph, and the absolute difference in height between two adjacent cells as the weight of the edge. Therefore, this problem is to solve the connectivity problem from the top-left node to the bottom-right node.
We first construct a set of edges, then sort them in ascending order of edge weight, and add edges one by one until the top-left node and the bottom-right node are connected. At this point, the weight of the edge is the minimum physical consumption value required by the problem.
The time complexity is
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.p = list(range(n))
self.size = [1] * n
def find(self, x):
if self.p[x] != x:
self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x])
return self.p[x]
def union(self, a, b):
pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b)
if pa == pb:
return False
if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]:
self.p[pb] = pa
self.size[pa] += self.size[pb]
else:
self.p[pa] = pb
self.size[pb] += self.size[pa]
return True
def connected(self, a, b):
return self.find(a) == self.find(b)
class Solution:
def minimumEffortPath(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(heights), len(heights[0])
uf = UnionFind(m * n)
e = []
dirs = (0, 1, 0)
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n:
e.append(
(abs(heights[i][j] - heights[x][y]), i * n + j, x * n + y)
)
e.sort()
for h, a, b in e:
uf.union(a, b)
if uf.connected(0, m * n - 1):
return h
return 0class UnionFind {
private final int[] p;
private final int[] size;
public UnionFind(int n) {
p = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
public boolean union(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
}
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
return true;
}
public boolean connected(int a, int b) {
return find(a) == find(b);
}
}
class Solution {
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(m * n);
List<int[]> edges = new ArrayList<>();
int[] dirs = {1, 0, 1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < 2; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
int d = Math.abs(heights[i][j] - heights[x][y]);
edges.add(new int[] {d, i * n + j, x * n + y});
}
}
}
}
Collections.sort(edges, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
for (int[] e : edges) {
uf.union(e[1], e[2]);
if (uf.connected(0, m * n - 1)) {
return e[0];
}
}
return 0;
}
}class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(int n) {
p = vector<int>(n);
size = vector<int>(n, 1);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
}
bool unite(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
}
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
return true;
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
bool connected(int a, int b) {
return find(a) == find(b);
}
private:
vector<int> p, size;
};
class Solution {
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int m = heights.size(), n = heights[0].size();
vector<array<int, 3>> edges;
int dirs[3] = {0, 1, 0};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < 2; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
edges.push_back({abs(heights[i][j] - heights[x][y]), i * n + j, x * n + y});
}
}
}
}
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
UnionFind uf(m * n);
for (auto& [h, a, b] : edges) {
uf.unite(a, b);
if (uf.connected(0, m * n - 1)) {
return h;
}
}
return 0;
}
};type unionFind struct {
p, size []int
}
func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind {
p := make([]int, n)
size := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
size[i] = 1
}
return &unionFind{p, size}
}
func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int {
if uf.p[x] != x {
uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x])
}
return uf.p[x]
}
func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool {
pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b)
if pa == pb {
return false
}
if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] {
uf.p[pb] = pa
uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb]
} else {
uf.p[pa] = pb
uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa]
}
return true
}
func (uf *unionFind) connected(a, b int) bool {
return uf.find(a) == uf.find(b)
}
func minimumEffortPath(heights [][]int) int {
m, n := len(heights), len(heights[0])
edges := make([][3]int, 0, m*n*2)
dirs := [3]int{0, 1, 0}
for i, row := range heights {
for j, h := range row {
for k := 0; k < 2; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n {
edges = append(edges, [3]int{abs(h - heights[x][y]), i*n + j, x*n + y})
}
}
}
}
sort.Slice(edges, func(i, j int) bool { return edges[i][0] < edges[j][0] })
uf := newUnionFind(m * n)
for _, e := range edges {
uf.union(e[1], e[2])
if uf.connected(0, m*n-1) {
return e[0]
}
}
return 0
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}class UnionFind {
private p: number[];
private size: number[];
constructor(n: number) {
this.p = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
this.size = Array(n).fill(1);
}
find(x: number): number {
if (this.p[x] !== x) {
this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]);
}
return this.p[x];
}
union(a: number, b: number): boolean {
const pa = this.find(a);
const pb = this.find(b);
if (pa === pb) {
return false;
}
if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) {
this.p[pb] = pa;
this.size[pa] += this.size[pb];
} else {
this.p[pa] = pb;
this.size[pb] += this.size[pa];
}
return true;
}
connected(a: number, b: number): boolean {
return this.find(a) === this.find(b);
}
}
function minimumEffortPath(heights: number[][]): number {
const m = heights.length;
const n = heights[0].length;
const uf = new UnionFind(m * n);
const edges: number[][] = [];
const dirs = [1, 0, 1];
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (let k = 0; k < 2; ++k) {
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
const d = Math.abs(heights[i][j] - heights[x][y]);
edges.push([d, i * n + j, x * n + y]);
}
}
}
}
edges.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
for (const [h, a, b] of edges) {
uf.union(a, b);
if (uf.connected(0, m * n - 1)) {
return h;
}
}
return 0;
}We notice that if the maximum physical consumption value of a path is
We define the left boundary of the binary search as
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def minimumEffortPath(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def check(h: int) -> bool:
q = deque([(0, 0)])
vis = {(0, 0)}
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
return True
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if (
0 <= x < m
and 0 <= y < n
and (x, y) not in vis
and abs(heights[i][j] - heights[x][y]) <= h
):
q.append((x, y))
vis.add((x, y))
return False
m, n = len(heights), len(heights[0])
return bisect_left(range(10**6), True, key=check)class Solution {
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int l = 0, r = 1000000;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(heights, mid)) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}
private boolean check(int[][] heights, int h) {
int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.add(new int[] {0, 0});
vis[0][0] = true;
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
var p = q.poll();
int i = p[0], j = p[1];
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return true;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y]
&& Math.abs(heights[x][y] - heights[i][j]) <= h) {
q.add(new int[] {x, y});
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
auto check = [&](int h) {
int m = heights.size(), n = heights[0].size();
bool vis[m][n];
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
queue<pair<int, int>> q{{{0, 0}}};
vis[0][0] = true;
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [i, j] = q.front();
q.pop();
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return true;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && abs(heights[x][y] - heights[i][j]) <= h) {
q.push({x, y});
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
return false;
};
int l = 0, r = 1e6;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}
};func minimumEffortPath(heights [][]int) int {
return sort.Search(1e6, func(h int) bool {
m, n := len(heights), len(heights[0])
vis := make([][]bool, m)
for i := range vis {
vis[i] = make([]bool, n)
}
vis[0][0] = true
q := [][2]int{}
q = append(q, [2]int{0, 0})
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
i, j := p[0], p[1]
if i == m-1 && j == n-1 {
return true
}
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && abs(heights[x][y]-heights[i][j]) <= h {
vis[x][y] = true
q = append(q, [2]int{x, y})
}
}
}
return false
})
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}function minimumEffortPath(heights: number[][]): number {
const check = (h: number): boolean => {
const m = heights.length;
const n = heights[0].length;
const vis: boolean[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(false));
const dirs: number[] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
const q: [number, number][] = [[0, 0]];
vis[0][0] = true;
while (q.length > 0) {
const [i, j] = q.pop()!;
if (i === m - 1 && j === n - 1) {
return true;
}
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (
x >= 0 &&
x < m &&
y >= 0 &&
y < n &&
!vis[x][y] &&
Math.abs(heights[x][y] - heights[i][j]) <= h
) {
q.push([x, y]);
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
return false;
};
let [l, r] = [0, 10 ** 6];
while (l < r) {
const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}We can treat each cell as a node in a graph, and the absolute difference in height between two adjacent cells as the weight of the edge. Therefore, this problem is to solve the shortest path problem from the top-left node to the bottom-right node.
We can use the Dijkstra algorithm to solve the shortest path problem, and use a priority queue (heap) to optimize the time complexity. Specifically, we maintain a two-dimensional array
We use a priority queue (heap) to store nodes, and each time we take out the node with the smallest weight from the priority queue (heap), then update the weights of its adjacent nodes. If the weight of an adjacent node changes, then we add this node to the priority queue (heap). When the priority queue (heap) is empty, it means that we have found the shortest path.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def minimumEffortPath(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(heights), len(heights[0])
dist = [[inf] * n for _ in range(m)]
dist[0][0] = 0
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
q = [(0, 0, 0)]
while q:
t, i, j = heappop(q)
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if (
0 <= x < m
and 0 <= y < n
and (d := max(t, abs(heights[i][j] - heights[x][y]))) < dist[x][y]
):
dist[x][y] = d
heappush(q, (d, x, y))
return int(dist[-1][-1])class Solution {
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
for (var row : dist) {
Arrays.fill(row, 1 << 30);
}
dist[0][0] = 0;
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
pq.offer(new int[] {0, 0, 0});
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
var p = pq.poll();
int t = p[0], i = p[1], j = p[2];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
int d = Math.max(t, Math.abs(heights[x][y] - heights[i][j]));
if (d < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = d;
pq.offer(new int[] {d, x, y});
}
}
}
}
return dist[m - 1][n - 1];
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int m = heights.size(), n = heights[0].size();
int dist[m][n];
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist));
dist[0][0] = 0;
int dirs[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
using T = tuple<int, int, int>;
priority_queue<T, vector<T>, greater<T>> pq;
pq.emplace(0, 0, 0);
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [t, i, j] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n) {
continue;
}
int d = max(t, abs(heights[x][y] - heights[i][j]));
if (d < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = d;
pq.emplace(d, x, y);
}
}
}
return dist[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};func minimumEffortPath(heights [][]int) int {
m, n := len(heights), len(heights[0])
dist := make([][]int, m)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range dist[i] {
dist[i][j] = 1 << 30
}
}
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
dist[0][0] = 0
pq := hp{}
heap.Push(&pq, tuple{0, 0, 0})
for pq.Len() > 0 {
p := heap.Pop(&pq).(tuple)
t, i, j := p.t, p.i, p.j
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n {
if d := max(t, abs(heights[x][y]-heights[i][j])); d < dist[x][y] {
dist[x][y] = d
heap.Push(&pq, tuple{d, x, y})
}
}
}
}
return dist[m-1][n-1]
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}
type tuple struct{ t, i, j int }
type hp []tuple
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].t < h[j].t }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v any) { *h = append(*h, v.(tuple)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() any { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }function minimumEffortPath(heights: number[][]): number {
const m = heights.length;
const n = heights[0].length;
const pq = new PriorityQueue({ compare: (a, b) => a[0] - b[0] });
pq.enqueue([0, 0, 0]);
const dist = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array.from({ length: n }, () => Infinity));
dist[0][0] = 0;
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
while (pq.size() > 0) {
const [t, i, j] = pq.dequeue()!;
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const [x, y] = [i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
const d = Math.max(t, Math.abs(heights[x][y] - heights[i][j]));
if (d < dist[x][y]) {
dist[x][y] = d;
pq.enqueue([d, x, y]);
}
}
}
}
return dist[m - 1][n - 1];
}