| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1596 |
第 320 场周赛 Q2 |
|
给你一个 二叉搜索树 的根节点 root ,和一个由正整数组成、长度为 n 的数组 queries 。
请你找出一个长度为 n 的 二维 答案数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] = [mini, maxi] :
mini是树中小于等于queries[i]的 最大值 。如果不存在这样的值,则使用-1代替。maxi是树中大于等于queries[i]的 最小值 。如果不存在这样的值,则使用-1代替。
返回数组 answer 。
示例 1 :
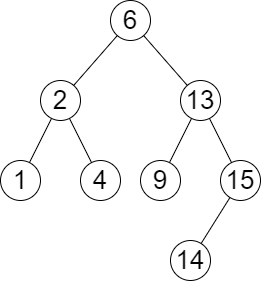
输入:root = [6,2,13,1,4,9,15,null,null,null,null,null,null,14], queries = [2,5,16] 输出:[[2,2],[4,6],[15,-1]] 解释:按下面的描述找出并返回查询的答案: - 树中小于等于 2 的最大值是 2 ,且大于等于 2 的最小值也是 2 。所以第一个查询的答案是 [2,2] 。 - 树中小于等于 5 的最大值是 4 ,且大于等于 5 的最小值是 6 。所以第二个查询的答案是 [4,6] 。 - 树中小于等于 16 的最大值是 15 ,且大于等于 16 的最小值不存在。所以第三个查询的答案是 [15,-1] 。
示例 2 :
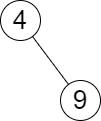
输入:root = [4,null,9], queries = [3] 输出:[[-1,4]] 解释:树中不存在小于等于 3 的最大值,且大于等于 3 的最小值是 4 。所以查询的答案是 [-1,4] 。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[2, 105]内 1 <= Node.val <= 106n == queries.length1 <= n <= 1051 <= queries[i] <= 106
由于题目中给出的是一棵二叉搜索树,因此我们可以通过中序遍历得到一个有序数组,然后对于每个查询,我们可以通过二分查找得到小于等于该查询值的最大值和大于等于该查询值的最小值。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def closestNodes(
self, root: Optional[TreeNode], queries: List[int]
) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode]):
if root is None:
return
dfs(root.left)
nums.append(root.val)
dfs(root.right)
nums = []
dfs(root)
ans = []
for x in queries:
i = bisect_left(nums, x + 1) - 1
j = bisect_left(nums, x)
mi = nums[i] if 0 <= i < len(nums) else -1
mx = nums[j] if 0 <= j < len(nums) else -1
ans.append([mi, mx])
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> closestNodes(TreeNode root, List<Integer> queries) {
dfs(root);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int x : queries) {
int i = Collections.binarySearch(nums, x + 1);
int j = Collections.binarySearch(nums, x);
i = i < 0 ? -i - 2 : i - 1;
j = j < 0 ? -j - 1 : j;
int mi = i >= 0 && i < nums.size() ? nums.get(i) : -1;
int mx = j >= 0 && j < nums.size() ? nums.get(j) : -1;
ans.add(List.of(mi, mx));
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
nums.add(root.val);
dfs(root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> closestNodes(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& queries) {
vector<int> nums;
function<void(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root->left);
nums.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->right);
};
dfs(root);
vector<vector<int>> ans;
int n = nums.size();
for (int& x : queries) {
int i = lower_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), x + 1) - nums.begin() - 1;
int j = lower_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), x) - nums.begin();
int mi = i >= 0 && i < n ? nums[i] : -1;
int mx = j >= 0 && j < n ? nums[j] : -1;
ans.push_back({mi, mx});
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func closestNodes(root *TreeNode, queries []int) (ans [][]int) {
nums := []int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs(root.Left)
nums = append(nums, root.Val)
dfs(root.Right)
}
dfs(root)
for _, x := range queries {
i := sort.SearchInts(nums, x+1) - 1
j := sort.SearchInts(nums, x)
mi, mx := -1, -1
if i >= 0 {
mi = nums[i]
}
if j < len(nums) {
mx = nums[j]
}
ans = append(ans, []int{mi, mx})
}
return
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function closestNodes(root: TreeNode | null, queries: number[]): number[][] {
const nums: number[] = [];
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
nums.push(root.val);
dfs(root.right);
};
const search = (x: number): number => {
let [l, r] = [0, nums.length];
while (l < r) {
const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (nums[mid] >= x) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
};
dfs(root);
const ans: number[][] = [];
for (const x of queries) {
const i = search(x + 1) - 1;
const j = search(x);
const mi = i >= 0 ? nums[i] : -1;
const mx = j < nums.length ? nums[j] : -1;
ans.push([mi, mx]);
}
return ans;
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
private List<int> nums = new List<int>();
public IList<IList<int>> ClosestNodes(TreeNode root, IList<int> queries) {
Dfs(root);
List<IList<int>> ans = new List<IList<int>>();
foreach (int x in queries) {
int i = nums.BinarySearch(x + 1);
int j = nums.BinarySearch(x);
i = i < 0 ? -i - 2 : i - 1;
j = j < 0 ? -j - 1 : j;
int mi = i >= 0 && i < nums.Count ? nums[i] : -1;
int mx = j >= 0 && j < nums.Count ? nums[j] : -1;
ans.Add(new List<int> {mi, mx});
}
return ans;
}
private void Dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Dfs(root.left);
nums.Add(root.val);
Dfs(root.right);
}
}