-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 717
Zebra dao接入指南
zebra-dao是对mybatis-spring的轻量级封装,mybatis-spring主要用于mybatis和spring进行整合。相关基础知识可参考:
mybatis中文官方文档:http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
mybatis-spring中文官方文档:http://www.mybatis.org/spring/zh/
在应用访问数据库的架构中,zebra-dao所处的位置如下所示:

zebra-dao具备原生mybatis或者mybatis-spring的所有功能,其用法本质上就是mybatis的用法。 此外,zebra-dao额外提供了:分页插件、异步化接口、多数据源等功能。
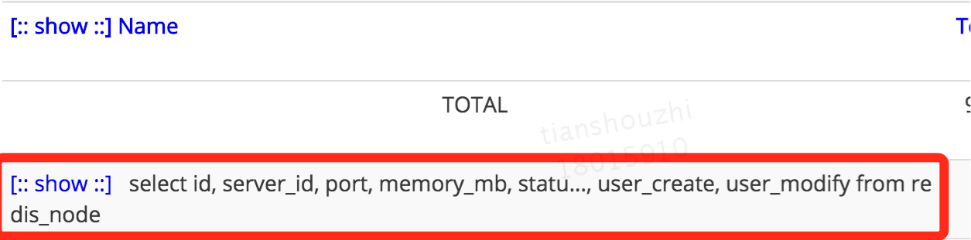
假如使用了zebra-dao,cat中的SQL显示的是类名+方法名;假如没有使用zebra-dao,cat中的SQL显示的是具体的sql语句。例如: service1使用zebra-dao:
而在service2中没有使用zebra-dao:

前者优于后者,因为前者能保证唯一且方便定位,而后者不方便定位代码,且当有相同sql语句时,无法判断是何处的代码。
<dependencies>
<!--zebra-dao依赖,其内部依赖了mybatis、mybatis-spring-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dianping.zebra</groupId>
<artifactId>zebra-dao</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Zebra数据源相关依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dianping.zebra</groupId>
<artifactId>zebra-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--zebra监控-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dianping.zebra</groupId>
<artifactId>zebra-cat-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Spring 相关依赖,请使用3.0以上版本-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
zebra-dao与spring整合主要分为3个步骤:
1、配置数据源,请参考:zebra读写分离接入指南如何配置一个GroupDataSource,或者分库分表接入指南如何配置一个ShardDataSource
2、配置SqlSessionFactoryBean
3、配置ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer。
注意:对于第3步要特别注意, 需要使用zebra-dao提供的ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer来替代mybatis-spring原生的MapperScannerConfigurer。
<!--第1步:配置数据源,省略-->
<!--第2步:配置SqlSessionFactoryBean-->
<bean id="zebraSqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--dataource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="datasource"/>
<!--Mapper files-->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:config/sqlmap/**/*.xml" />
<!--这里改成实际entity目录,如果有多个,可以用,;\t\n进行分割-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.xmd.xxx.entity" />
</bean>
<!--第3步:配置ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer-->
<bean class="com.dianping.zebra.dao.mybatis.ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer">
<!--这里改成实际dao目录,如果有多个,可以用,;\t\n进行分割-->
<property name="basePackage" value="com.xmd.xxx.dao" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="zebraSqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
@Configuration
public class ZebraConfiguration {
//第1步:配置数据源,省略
//第2步:配置SqlSessionFactoryBean
@Bean(name="zebraSqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
ssfb.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources("classpath*:config/sqlmap/**/*.xml"));
ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.xmd.xxx.entity");
return ssfb;
}
//第3步:配置ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer
@Bean
public ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer() throws IOException {
ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer configurer = new ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer();
configurer.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName("zebraSqlSessionFactory");
configurer.setBasePackage("com.xmd.xxx.dao");
return configurer;
}
}
zebra-dao的附加功能主要是为了方便使用提供的一些功能。用户可以根据自己的实际情况,选择是否接入。
对于一些复杂的业务,一个应用中可能需要访问多个库,对应的就需要有多个数据源,每个数据源访问不同的库。原始的mybatis多数据源配置比较复杂,针对每个数据源(DataSource)配置,都需要配置对应的SqlSessionFactory和MapperScannerConfigurer。 zebra-dao中,提供了ZebraRoutingDataSource以支持多数据源的配置,@ZebraRouting注解支持在任意bean的类上或者方法上使用,且支持了事务。
<!--1、定义两个GroupDataSource数据源-->
<bean id="zebraDataSource" class="com.dianping.zebra.group.jdbc.GroupDataSource"
init-method="init">
<property name="jdbcRef" value="zebra" />
<!--其他属性...-->
</bean>
<bean id="zebra_utDataSource" class="com.dianping.zebra.group.jdbc.GroupDataSource"
init-method="init">
<property name="jdbcRef" value="zebra_ut" />
<!--其他属性...-->
</bean>
<!--2、配置RoutingDataSource-->
<bean id="routingDatasource" class="com.dianping.zebra.dao.datasource.ZebraRoutingDataSource">
<property name="targetDataSources">
<!--其中key属性将在后面的@ZebraRouting注解中使用到-->
<map>
<entry key="zebra" value-ref="zebraDataSource"/>
<entry key="zebra_ut" value-ref="zebra_utDataSource"/>
</map>
</property>
<!--在为指定的情况下,默认走的数据源-->
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" value="zebra_ut"/>
</bean>
<!--3、配置SqlSessionFactoryBean,注意dataSource属性引用的是RoutingDataSource-->
<bean id="zebraSqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="routingDatasource" />
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:config/sqlmap/**/*.xml" />
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.dianping.zebra.dao.entity" />
</bean>
<!--4、配置ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer-->
<bean class="com.dianping.zebra.dao.mybatis.ZebraMapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="zebraSqlSessionFactory"/>
<property name="basePackage" value="com.dianping.zebra.dao.mapper"/>
</bean>
方式一:使用@ZebraRouting注解
注意:@ZebraRouting注解必须加载public方法上。接口中定义的方法,public可省略。
- 方法上添加@ZebraRouting注解:
public interface TestMapper{
//通过@Routing注解,指定此方法走zebra_ut数据源
@ZebraRouting("zebra_ut")
TestEntity findById(int id);
//未添加注解,将走默认的数据源zebra_ut
TestEntity findAll();
}
- 接口上添加@ZebraRouting注解 下面接口中定义的2个方法都会走数据源zebra_ut数据源。
@ZebraRouting("zebra_ut")
public interface TestMapper extends ZebraUTMapper{
TestEntity findById(int id);
TestEntity findAll();
}
- 接口/方法上同时添加@ZebraRouting注解 方法上的@ZebraRouting注解优先于接口上的@ZebraRouting注解
@ZebraRouting("zebra_ut")
public interface TestMapper extends ZebraUTMapper{
//使用方法上@ZebraRouting注解指定的zebra数据源
@ZebraRouting("zebra")
TestEntity findById(int id);
//使用接口上@ZebraRouting注解指定的zebra数据源
TestEntity findAll();
}
方式二:使用包名
如果操作不同的库的Mapper接口位于不同的包下面,例如:
-
操作zebra库的Mapper接口都位于com.dianping.zebra.dao.mapper.zebra包下
-
操作zebra_ut库的Mapper接口有位于com.dianping.zebra.dao.mapper.zebra_ut包下
此时我们可以修改RoutingDataSource的配置,如下:
<bean id="routingDatasource" class="com.dianping.zebra.dao.datasource.ZebraRoutingDataSource">
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map>
<entry key="zebra" value-ref="zebraDataSource"/>
<entry key="zebra_ut" value-ref="zebra_utDataSource"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" value="zebra_ut"/>
<!--指定不同包下的Mapper映射接口使用不同的数据源-->
<property name="packageDataSourceKeyMap">
<map>
<entry key="com.dianping.zebra.dao.mapper.zebra" value="zebra"/>
<entry key="com.dianping.zebra.dao.mapper.zebra_ut" value="zebra_ut"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
通过这种方式,简化了配置,不需要在每个Mapper接口或者方法上添加@Routing注解。
如果依然使用了@ZebraRouting注解,则优先级如下:方法级别的@ZebraRouting注解 > 接口级别的@ZebraRouting注解 >包级别的指定 >默认
ZebraRoutingDataSource支持与spring事务整合,以下以声明式事务为例:
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--注意事务管理器的dataSource属性指定的也是RoutingDataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="routingDatasource" />
</bean>
之后,在业务层的方法上,我们可以同时添加@Transactional注解和@ZebraRouting注解,如下:
public class RoutingService{
@Transactional
@ZebraRouting("zebra")
pubic void xxx(){
//此方法里面所有Mapper接口,都只能操作zebra数据源访问的库中的表,如果操作其他库的表,将会报错
//意味着将忽略内部调用的Mapper映射器接口上的@Routing注解
}
@Transactional
@ZebraRouting("zebra_ut")
pubic void yyy(){
//此方法里面所有Mapper接口,都只能操作zebra_ut数据源访问的库中的表,如果操作其他库的表,将会报错
}
@Transactional
pubic void zzz(){
//如果使用了事务,但是没有指定@ZebraRouting注解,将使用默认的数据源开启事务 ,不建议这种使用方式,建议在使用事务的情况下,总是显示的添加@ZebraRouting注解
}
pubic void xyz(){
//没有使用事务,且没有注解,则由内部Mapper映射器接口上@ZebraRouting注解,决定访问哪一个库
}
@ZebraRouting("zebra")
pubic void xyz(){
//没有使用事务,但是使用了@ZebraRouting注解,
//此方法里面调用的所有Mapper接口,都只能操作zebra数据源访问的库中的表,如果操作其他库的表,将会报错
}
}
逻辑分页是指将数据库中的所有数据取出到内存中,然后通过Java代码控制分页。一般是通过JDBC协议中定位游标的位置进行操作的,使用absolute方法。MyBatis中原生也是通过这种方式进行分页的。下面举例说明:
在HeartbeatMapper.xml中
<select id="getAll" parameterType="map" resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat
</select>
在HeartbeatMapper.java中,使用RowBounds中定义分页的offset和limit:
List<HeartbeatEntity> getAll(RowBounds rb);
该功能是MyBatis原生支持,业务可以直接使用。
物理分页指的是在SQL查询过程中实现分页,依托与不同的数据库厂商,实现也会不同。zebra-dao扩展了一个拦截器,实现了改写SQL达到了物理分页的功能。下面举例说明如何使用: 1.修改Spring的配置中的sqlSessionFactory,添加configLocation
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:config/mybatis/mybatis-configuration.xml" />
</bean>
2.增加mybatis-configuration.xml文件,目前zebra-dao只实现了MySQLDialect。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.dianping.zebra.dao.plugin.page.PageInterceptor">
<property name="dialectClass" value="com.dianping.zebra.dao.dialect.MySQLDialect"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>
如此配置后,所有的分页查询都变成物理分页了。
zebra-dao支持在一个dao调用中同时获得总条数和数据。举例来说: 在HeartbeatMapper.xml中:
<select id="getAll" parameterType="map" resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat
</select>
在HeartbeatMapper.java中,可以使用PageModel定义page和pageNum,同时使用这个对象就可以获得recordCount(总数)和records(结果数据)。注意的是,这个功能必须要配置过物理分页才能支持。
// must return void
void getAll(PageModel page);
注意这里没有任何返回值,返回的值在PageModel对象里面。一旦使用了PageModel的方式,必须是配置了物理分页,并且方法的返回值必须为void。
使用RowBounds的方式
对于回调和Future都支持。
回调支持: RowBoundsWithCallback
dao.getPage(new RowBounds(0, 100), new AsyncDaoCallback<List<HeartbeatEntity>>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(List<HeartbeatEntity> result) {
System.out.println(result.size());
Assert.assertEquals(100, result.size());
}
@Override
public void onException(Exception e) {
}
});
Future支持:
RowBoundsWithFuture
Future<List<HeartbeatEntity>> page = dao.getPage(new RowBounds(0, 100));
List<HeartbeatEntity> list = page.get();
使用PageModel的方式
仅仅支持回调的方式,不支持Future的方式。在回调方式使用中,回调方法onSuccess中传入的PageModel并不是结果,结果在调用dao时传入的model中。 Server
/* 参数 model,AsyncDaoCallback<T>
* 返回值 void
* 通过AsyncDaoCallback处理结果
* 成功 onSuccess(PageModel p) 结果装载在model中
* 失败 onEsception(Exception e) */
clusterDao.findAllCluster (model, new AsyncDaoCallback<PageModel>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(PageModel pageModel) {
//pageModel为null,real result is in the model
model.getRecordCount();
model.getRecords().size();
}
@Override
public void onException(Exception e) {
//todo
}
});
PageModel方式
除PageModel不带其他参数
PageModel paginate = new PageModel(2, 100); // public PageModel(int page, int pageSize);
dao.getAll(paginate);
//对应xml配置
<select id="getAll" parameterType="map" resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat
</select>
除PageModel带其他参数
- 动态SQL
PageModel paginate = new PageModel(2, 100);
dao.getAllWithAppNameAndDynamicSQL(paginate, "taurus-agent");
//对应xml配置
<select id="getAllWithAppNameAndDynamicSQL" parameterType="map" resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat
<if test="appName != null">Where `app_name` = #{appName}</if>
</select>
- 非动态SQL
PageModel paginate = new PageModel(2, 100);
dao.getAllWithAppName(paginate,"taurus-agent");
//对应xml配置
<select id="getAllWithAppName" parameterType="map" resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat Where `app_name` = #{appName}
</select>
参数为复杂类型参数
- 动态SQL:
PageModel paginate = new PageModel(2, 100);
QueryCondition condition = new QueryCondition("taurus-agent");
dao.getAllWithQueryCondition(paginate,condition);
//对应xml配置
<select id="getAllWithQueryCondition" parameterType="com.dianping.zebra.dao.mapper.QueryCondition"
resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat
<if test="appName != null">Where `app_name` = #{appName}</if>
</select>
- 非动态SQL
PageModel paginate = new PageModel(2, 100);
QueryCondition condition = new QueryCondition("taurus-agent");
dao.getAllWithQueryConditionWithoutDynamicSQL(paginate,condition);
//对应xml配置
<select id="getAllWithQueryConditionWithoutDynamicSQL" parameterType="com.dianping.zebra.dao.mapper.QueryCondition"
resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat
Where `app_name` = #{appName}
</select>
RowBounds方式(mybatis原生支持) 除RowBounds外的其他参数调用与PageModel方式类似,这里举2个例子:
- RowBounds + 动态SQL + 简单数据类型
List<HeartbeatEntity> rows = dao.getPageWithDynamicSQL(new RowBounds(0, 100), "taurus-agent");
//对应xml配置
<select id="getPageWithDynamicSQL" resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat
<if test="appName != null">Where `app_name` = #{appName}</if>
</select>
- RowBounds + 动态SQL + 复杂数据类型
QueryCondition condition = new QueryCondition("taurus-agent");
List<HeartbeatEntity> rows = dao.getPageWithDynamicSQLAndQueryCondition(new RowBounds(0, 100), condition);
//对应xml配置
<select id="getPageWithDynamicSQLAndQueryCondition" parameterType="com.dianping.zebra.dao.mapper.QueryCondition"
resultType="HeartbeatEntity">
SELECT * FROM heartbeat
<if test="appName != null">Where `app_name` = #{appName}</if>
</select>
使用高级物理分页(PageModel)时,不支持:
SQL使用join
查询参数不支持List类型参数
不支持分组统计(即group by)
如果属于这几种情况,请不要使用zebra的分页插件