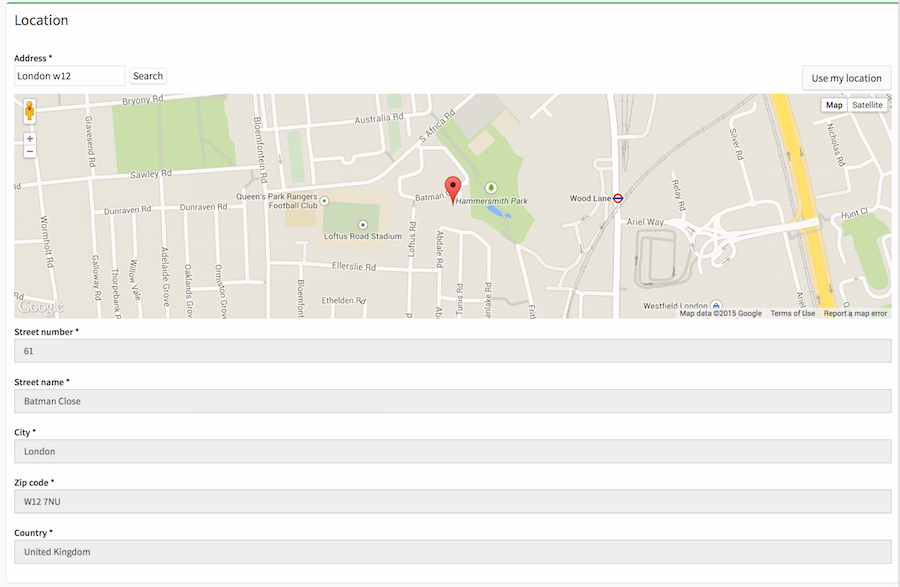
This is a Symfony bundle which facilitates making entities addressable and geo location aware.
It includes a google map form type to search for and set addresses (with lat/lng), and a geo spatial service to ease calculating distances, sorting and filtering within a radius, etc using these objects with latitude and longitude.
Add the following to composer.json:
"require": {
...
"daa/addressable-bundle": "^0.6"
}Register the bundle in your config/bundles.php:
return [
...
Addressable\Bundle\AddressableBundle::class => ['all' => true]
]Include the twig template for the type layout in config/packages/twig.yml
twig:
default_path: '%kernel.project_dir%/templates'
form_themes:
- '@Addressable/Form/fields.html.twig'Add the following to composer.json:
"require": {
...
"daa/addressable-bundle": "0.5"
}Register the bundle in your app/AppKernel.php:
new Addressable\Bundle\AddressableBundle(),Include the twig template for the type layout in app/config/config.yml
twig:
form_themes:
- '@Addressable/Form/fields.html.twig' # or AddressableBundle:Form:fields.html.twig in older versions of symfonyNow your entity or document must:
- implement the included AddressableInterface
- use the relevant trait (ORM or PHPCR version) or manually reproduce the required fields, getters and setters
namespace Your\Project\Entity;
use Addressable\Bundle\Model\AddressableInterface;
use Addressable\Bundle\Model\Traits\ORM\AddressableTrait;
# for optional email, tel, fax fields also include and use these
use Addressable\Bundle\Model\ContactableInterface;
use Addressable\Bundle\Model\Traits\ORM\ContactableTrait;
class YourEntity implements AddressableInterface, ContactableInterface
{
use AddressableTrait;
use ContactableTrait;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="text")
*/
protected $yourOtherField;
...
}Note, if you are using an older version of PHP which does not support traits, then you are forced to copy the trait code manually into your entity.
Once your entity is setup, we can add the address map selector to your forms in the following ways:
use Addressable\Bundle\Form\Type\AddressMapType;
use Addressable\Bundle\Form\Type\ContactDetailsType; # optional email, tel, fax
// if you are using standard symfony form type
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('address', AddressMapType::class, array(
'google_api_key' => 'yourKeyHere'
))
...
}
// if you are using Sonata Admin
protected function configureFormFields(FormMapper $formMapper)
{
$formMapper
->with('Location')
->add('address', AddressMapType::class, array(
'google_api_key' => 'yourKeyHere'
))
->end()
...
}
/**
* if you are doing it directly in a controller Action
*
* @Route("/", name="homepage")
* @Template("@App/page.html.twig")
*/
public function indexAction(Request $request)
{
$entity = new AddressableEntity();
$form = $this->createForm(AddressMapType::class, $entity, array(
'google_api_key' => 'yourKeyHere'
));
/* or alternatively when using the nested/related versions:
$form = $this->createFormBuilder($entity)
->add('address', AddressMapType::class, array(
'google_api_key' => 'yourKeyHere'
))
->add('contactDetails', ContactDetailsType::class)
->getForm();
*/
// replace this example code with whatever you need
return [
'form' => $form->createView(),
];
}Note: if using address as a child or relation remember to set the 'data_class' options pointing to the Address object.
We can override several options:
->add(
'address',
AddressMapType::class,
array(
'google_api_key' => 'yourKeyHere',
'map_width' => '100%', // the width of the map
'map_height' => '300px', // the height of the map
'default_lat' => 51.5, // the starting position on the map
'default_lng' => -0.1245, // the starting position on the map
'include_current_position_action' => true, // whether to include the set current position button
'street_number_field' => array(
'name' => 'streetNumber',
'type' => 'text',
'options' => array(
'required' => true
)
),
'street_name_field' => array(
'name' => 'streetName',
'type' => 'text',
'options' => array(
'required' => true
)
),
'city_field' => array(
'name' => 'city',
'type' => 'text',
'options' => array(
'required' => true
)
),
'zipcode_field' => array(
'name' => 'zipCode',
'type' => 'text',
'options' => array(
'required' => true
)
),
'country_field' => array(
'name' => 'country',
'type' => 'text',
'options' => array(
'required' => true
)
),
'latitude_field' => array(
'name' => 'latitude',
'type' => 'hidden',
'options' => array(
'required' => false
)
),
'longitude_field' => array(
'name' => 'longitude',
'type' => 'hidden',
'options' => array(
'required' => false
)
),
'administrative_area_level_1_field' => array(
'name' => 'administrativeAreaLevel1',
'type' => 'text',
'options' => array(
'required' => false
)
),
'administrative_area_level_2_field' => array(
'name' => 'administrativeAreaLevel2',
'type' => 'text',
'options' => array(
'required' => false
)
)
)
);
# And same for the optional contact details fields
->add(
'contactDetails',
ContactDetailsType:class,
array(
'email_field' => array(
'name' => 'email',
'type' => TextType::class,
'options' => array(
'required' => false
)
),
'phone_field' => array(
'name' => 'phoneNumber',
'type' => TextType::class,
'options' => array(
'required' => false
)
),
'fax_field' => array(
'name' => 'fax',
'type' => TextType::class,
'options' => array(
'required' => false
)
),
)
);If you use "country" type (Symfony\Component\Form\Extension\Core\Type\CountryType) for the "country_field" the geospatial helper uses googles returned shortcode to populate the country short code in the dropdown
If you don't want the bundle to use it's own script you can override the address_map_scripts block to be empty; and then simply copy and paste the javascript in vendor/daa/addressable-bundle/Resources/public/js/address_map.js to your own js files.
To add additional functionality after address updates, simply override the block address_map_callback and extend to add the additional functionality (or make it empty and define var gmap_callback in your js code).
{% block address_map_callback %}
<script>
var gmap_callback = function(location, gmap){
// your callback code here
}
</script>
{% endblock %}
Sonata implementation:
From your controller you can get the the addressable_bundle.geospatial_helper service; from anywhere else you can instantiate the GeospatialHelper class directly.
Examples:
public function symfonyControllerAction()
{
$helper = $this->get('addressable_bundle.geospatial_helper');
$centerPoint = new YourEntity(); // must implement AddressableInterface or GeoPointInterface
$point1 = new YourEntity(); // must implement AddressableInterface or GeoPointInterface
$point2 = new YourEntity(); // must implement AddressableInterface or GeoPointInterface
$points = array($point1, $point2);
// getting distance in KM between two points
$distanceInKm = $helper->getDistanceBetweenPoints($point1, $point2);
// filtering an array of points by radius from a center point
$pointsWithinRadius = $helper->filterPointsWithinRadius($centerPoint, $points, $radius);
// sort an array of addressable objects to be ordered by distance from a center point
$orderedPoints = $helper->sortAroundCenterPoint($centerPoint, $points);
}