-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 9
Topic Modelling
LDA is an algorithm that is used to discover the topics that are in a text. Topic modeling is an unsupervised model for detecting topics in a corpus and categorizing similar texts. Assume that you have some documents, for example Government Gazette Documents, and you want to cluster them to similar topics, hence LDA is a perfect fit. The algorithms work in a different way regarding their mathematics. We are going to use sklearn for topic modeling and clustering to similar topics.
According to [4], in LDA, each document may be viewed as a mixture of various topics where each document is considered to have a set of topics that are assigned to it via LDA. This is identical to probabilistic latent semantic analysis (pLSA), except that in LDA the topic distribution is assumed to have a sparse Dirichlet prior. The sparse Dirichlet priors encode the intuition that documents cover only a small set of topics and that topics use only a small set of words frequently. In practice, this results in a better disambiguation of words and a more precise assignment of documents to topics. LDA is a generalization of the pLSA model, which is equivalent to LDA under a uniform Dirichlet prior distribution.
The code is located at 3gm/topic_models.py
The proposed way of modeling the topics is:
- Parse raw texts
- Remove punctuation numbers
- Filter out words considered "junk" (i.e. really small words)
- Lemmatize everything using Greek Lemmatizer provided from this GSoC project which adds the Greek Language to spaCy and lookup provided at
resources/greek_lemmas.py. - Run LDA to extract topics (optionally using grid search) to find the best parameters
- Gather topics to a graph.
- Store to MongoDB collection.
The pipeline is illustrated below:
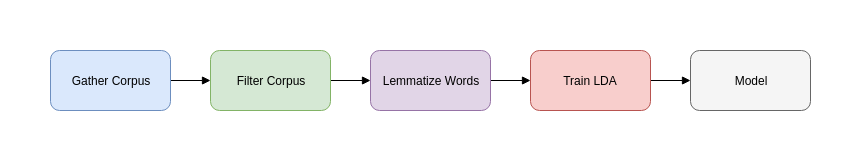
We can further our work by searching for connected components in the graph using a graph search algorithm such as Breadth-First Search.
A visualization of topic models can finally be done using the pyLDAvis library.
The topic_models.py module populates everything from the database. Invoking it via
python3 topic_models.py
would build the topics for your codifier corpus. You can adjust the parameters n_components and no_top_words to see how the model performs, as well as the bounds for the Greek stoplist and the Government Gazette stoplist.
Then it builds the topics collection to the MongoDB database:
For example the query
{'statutes' : 'ν. 4009/2011'}
yields the following topic
{
"_id":79,
"statutes":[
"π.δ. 14/2017",
"ν. 4009/2011",
"ν. 3848/2010",
"ν. 4473/2017",
"ν. 4415/2016",
"ν. 4115/2013",
"π.δ. 47/2006",
"ν. 3467/2006",
"ν. 4395/2016",
"ν. 3413/2005",
"π.δ. 96/2012",
"ν. 3685/2008",
"π.δ. 28/2014",
"ν. 4386/2016",
"ν. 4283/2014",
"π.δ. 78/2016",
"π.δ. 9/2006",
"π.δ. 173/2008",
"π.δ. 155/2007",
"ν. 4485/2017",
"ν. 3748/2009",
"ν. 4476/2017",
"ν. 4452/2017",
"ν. 4310/2014",
"π.δ. 252/2005",
"ν. 3794/2009",
"π.δ. 41/2011",
"π.δ. 89/2015",
"π.δ. 54/2012"
],
"keywords":[
"παιδείας",
"θρησκευμάτων",
"εκπαίδευσης",
"έρευνας",
"πολιτισμού",
"διευθυντής",
"αθλητισμού",
"σπουδών",
"ιδρύματος",
"αθλητής",
"τομέα",
"εκπαιδευτικοί",
"σχόλη",
"μάθησης",
"βίου",
"συμβούλιο",
"ακαδημαϊκά",
"διευθυντή",
"διδακτά",
"προγράμματος",
"καθηγητής",
"βαθμίδα",
"ινστιτούτο",
"σχολής",
"υπουργού",
"συμβουλίου",
"φοιτητής",
"προσωπικού",
"εφημερίδα",
"υπουργείου",
"κυβερνήσεως",
"δι",
"τμήματος",
"οργανισμό",
"εθνικής",
"οργανισμού",
"έρευνα",
"σχολή",
"αλλοδαπή",
"κριτήρια",
"συγκρότηση",
"τεχνολογία",
"προσόντα",
"ημεδαπά",
"κέντρου",
"τεχνολογίας",
"διεύθυνση",
"κατ",
"πιστοποίηση",
"ερευνών",
"τόμε",
"κατάρτισης",
"υπουργό",
"προσόντων",
"διεθνές",
"σχολές",
"υποψηφίων",
"εξέλιξη",
"αναγνωρισμένος",
"γνώστης",
"πανεπιστημίου",
"κατεύθυνση",
"υπουργών",
"γραφείο",
"τμημάτων",
"δίπλωμα",
"εισαγωγή",
"ίδρυση",
"ειδικού",
"υποψήφιος",
"διεξαγωγή",
"προγραμμάτων",
"ολοκλήρωση",
"εξωτερικά",
"οργανισμός",
"αμοιβή",
"κατανομή",
"τοποθέτηση",
"ποιότητα",
"εξαίρεση",
"εδες",
"απόσπαση",
"διατάξεις",
"εθνικό",
"νοούμαι",
"απασχόληση",
"παρ",
"στέλεχος",
"σκόπια",
"κυκλικά",
"εξάμηνο",
"γλώσσας",
"εκπόνηση",
"εργαστηρίων",
"αξιοποίηση",
"πίνακες",
"καθήκοντα",
"ακολούθως",
"συμμετέχω",
"εποπτεύω"
]
} For further improving the lemmatization process for topic extraction we are also using the spaCy's lemmatizer for the Greek Language via the word.lemma_ attribute.
In case you want to invoke spaCy's lemmatizer along with the lookup, you can do this by running:
python3 topic_models.py --spacy - Medium Article
- sklearn Reference Manual
- Blei, David M., Andrew Y. Ng, and Michael I. Jordan. "Latent dirichlet allocation." Journal of machine Learning research 3.Jan (2003): 993-1022.
- Latent Dirichlet Allocation, Wikipedia
- Getting started
- Algorithms
- Datasets and Continuous Integration
- Documentation
- Development