-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 579
[Examples] Assign a Built in Policy
This page describes how to assign built-in Azure Policies to your environment using the caf-enterprise-scale module.
In this example you will use two built-in policies and one built-in policy set definition. You will use policies that are not already available for assignment via the default Enterprise Scale deployment.
The policies you will use are Not allowed resource types and Deploy default Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension for Windows Server.
The policy set definition (Initiative) you will use is NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5.
NOTE: You can view which policies are recommended to be assigned as part of an Enterprise Scale deployment here.
You will update the built-in configuration by following these steps:
- Create the policy assignment files for
Not allowed resource types,Deploy default Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension for Windows ServerandNIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5. You will also configure thelistOfResourceTypesNotAllowedparameter within theNot allowed resource typesassignment file to prevent the creation of Azure Firewalls - Assign the policy definition for
Deploy default Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension for Windows Serverat thees_rootManagement Group by extending the built-in archetype fores_root - Assign the policy set definition for
NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5at thees_rootManagement Group by extending the built-in archetype fores_root - Assign the policy definition for
Not allowed resource typesat theLanding ZonesManagement Group by extending the built-in archetype fores_landing_zones.
IMPORTANT: To allow the declaration of custom or expanded templates, you must create a custom library folder within the root module and include the path to this folder using the
library_pathvariable within the module configuration. In our example, the directory is/lib.
In order to assign built-in policies, there needs to be an assignment file for each policy or policy set definition that we want to use.
This module already includes assignment files for some built-in policies so it's important to check whether or not one exists before creating your own.
You can do this by navigating to \modules\archetypes\lib\policy_assignments and looking for an assignment file that matches the policy you want to assign.
An example of a built-in policy that already has an assignment file included within the module is the Kubernetes clusters should be accessible only over HTTPS policy. The assignment file for this policy is named policy_assignment_es_deny_http_ingress_aks.tmpl.json.
NOTE: You can view the module lib directly here
As the policies you will use in this example do not already have an assignment file within the module, you will need to create the below files so that you can assign them:
- ./lib/policy_assignments/policy_assignment_not_allowed_resource_types.json
- ./lib/policy_assignments/policy_assignment_deploy_default_microsoft_IaaSAntimalware_extension_for_windows_server.json
- ./lib/policy_assignments/policy_assignment_nist_sp_800_53_rev_5.json
In order to assign built-in policies or policy sets, you need to create policy assignment files. The first step is to create a policy_assignments subdirectory within /lib.
NOTE: Creating a
policy_assignmentssubdirectory within\libis a recommendation only. If you prefer not to create one or to call it something else, the custom policies will still work.
You will then need to create a file named policy_assignment_not_allowed_resource_types.json within the policy_assignments directory. Copy the below code in to the file and save it.
NOTE: The full file name is not important but it does need to meet the naming conventions detailed here
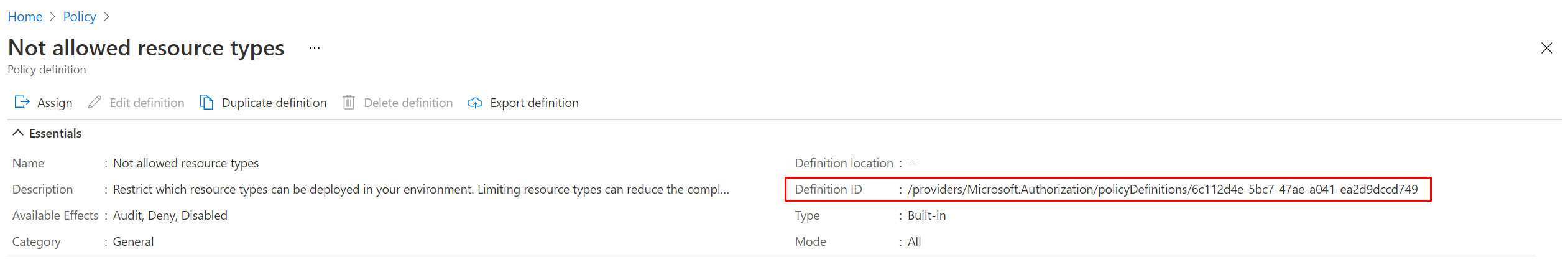
To assign the correct policy, we need to provide the appropriate value for policyDefinitionID within our assignment file. You can retrieve the PolicyDefinitionID for your policy either through the Azure Portal, Azure PowerShell or the Azure CLI
{
"name": "Not-Allowed-Resources",
"type": "Microsoft.Authorization/policyAssignments",
"apiVersion": "2019-09-01",
"properties": {
"description": "Restrict which resource types can be deployed in your environment. Limiting resource types can reduce the complexity and attack surface of your environment while also helping to manage costs. Compliance results are only shown for non-compliant resources.",
"displayName": "Not allowed resources",
"notScopes": [],
"parameters": {
"listOfResourceTypesNotAllowed":{
"value": ["Microsoft.Network/azureFirewalls"]
}
},
"policyDefinitionId": "/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/policyDefinitions/6c112d4e-5bc7-47ae-a041-ea2d9dccd749",
"nonComplianceMessages": [
{
"message": "Resources {enforcementMode} not be in the specified types."
}
],
"scope": "${current_scope_resource_id}",
"enforcementMode": null
},
"location": "${default_location}",
"identity": {
"type": "None"
}
}IMPORTANT: The name parameter in the assignment file has an upper limit of 24 characters. Values longer than this will result in a validation error. As an example, "Not allowed resources fits but "Not allowed resource types" would result in an error.
Now create a file named policy_assignment_deploy_default_microsoft_IaaSAntimalware_extension_for_windows_server.json within the policy_assignments directory. Copy the below code in to the file and save it.
NOTE: As this policy has an effect type of
DeployIfNotExists, you also need to tell the module to create a System Assigned Managed Identity for the policy to use. This is done within the assignment file and would also be needed for any policy with aModifyeffect type.
lib/policy_assignments/policy_assignment_deploy_default_microsoft_IaaSAntimalware_extension_for_windows_server.json
{
"name": "Deploy-Antimalware-Ext",
"type": "Microsoft.Authorization/policyAssignments",
"apiVersion": "2019-09-01",
"properties": {
"description": "This policy deploys a Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension with a default configuration when a VM is not configured with the antimalware extension.",
"displayName": "Deploy default Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension for Windows Server",
"notScopes": [],
"parameters": {
},
"policyDefinitionId": "/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/policyDefinitions/2835b622-407b-4114-9198-6f7064cbe0dc",
"nonComplianceMessages": [
{
"message": "Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension {enforcementMode} be deployed when a VM is not configured with antimalware."
}
],
"scope": "${current_scope_resource_id}",
"enforcementMode": null
},
"location": "${default_location}",
"identity": {
"type": "SystemAssigned"
}
}Finally, create an assignment file for the policy set named policy_assignment_nist_sp_800_53_rev_5.json within the policy_assignments directory. Copy the below code in to the file and save it.
{
"name": "NIST-SP-800-53-Rev5",
"type": "Microsoft.Authorization/policyAssignments",
"apiVersion": "2019-09-01",
"properties": {
"description": "This initiative includes policies that address a subset of NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5 controls. Additional policies will be added in upcoming releases. For more information, visit https://aka.ms/nist800-53r5-initiative.",
"displayName": "NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5",
"notScopes": [],
"parameters": {
},
"policyDefinitionId": "/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/policySetDefinitions/179d1daa-458f-4e47-8086-2a68d0d6c38f",
"nonComplianceMessages": [
{
"message": "NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5 controls {enforcementMode} be enforced"
}
],
"scope": "${current_scope_resource_id}",
"enforcementMode": null
},
"location": "${default_location}",
"identity": {
"type": "SystemAssigned"
}
}Assign the Deploy default Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension for Windows Server Policy at the es_root Management Group
You now need to assign the Deploy default Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension for Windows Server policy and in this example, we will assign it at es_root. If you don't already have an archetype_extension_es_root.tmpl.json file within your custom /lib directory, create one and copy the below code in to the file.
{
"extend_es_root": {
"policy_assignments": ["Deploy-Antimalware-Ext"],
"policy_definitions": [],
"policy_set_definitions": [],
"role_definitions": [],
"archetype_config": {
"access_control": {
}
}
}
}You should now kick-off your Terraform workflow (init, plan, apply) to apply the new configuration. This can be done either locally or through a pipeline. When your workflow has finished, the Deploy default Microsoft IaaSAntimalware extension for Windows Server policy will be assigned at es_root.
You now need to assign the NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5 policy set and in this example, we will assign it at es_root. Copy the below code in to your archetype_extension_es_root.tmpl.json file and save it.
{
"extend_es_root": {
"policy_assignments": ["Deploy-Antimalware-Ext", "NIST-SP-800-53-Rev5"],
"policy_definitions": [],
"policy_set_definitions": [],
"role_definitions": [],
"archetype_config": {
"access_control": {
}
}
}
}You should now kick-off your Terraform workflow (init, plan, apply) to apply the new configuration. This can be done either locally or through a pipeline. When your workflow has finished, the NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5 policy set will be assigned at es_root.
In this example, we will assign it at the Landing Zones Management Group. To do this, either update your existing archetype_extension_es_landing_zones.tmpl.json file or create one and copy the below code in to it and save.
{
"extend_es_landing_zones": {
"policy_assignments": ["Not-Allowed-Resources"],
"policy_definitions": [],
"policy_set_definitions": [],
"role_definitions": [],
"archetype_config": {
"access_control": {
}
}
}
}You should now kick-off your Terraform workflow once again to apply the updated configuration. This can be done either locally or through a pipeline. When your workflow has finished, the Not allowed resource types policy will be assigned at the Landing Zones Management Group.
You have now successfully assigned a built-in Policy Definition and a built-in Policy Set Definition within your Azure environment. You can re-use the guidance in this article for any other built-in policies that you may wish to use within your environment.
This wiki is being actively developed
If you discover any documentation bugs or would like to request new content, please raise them as an issue or feel free to contribute to the wiki via a pull request. The wiki docs are located in the repository in the docs/wiki/ folder.
- Home
- User guide
- Video guides
-
Examples
- Level 100
- Level 200
-
Level 300
- Deploy multi region networking with custom settings (Hub and Spoke)
- Deploy multi region networking with custom settings (Virtual WAN)
- Deploy with Zero Trust network principles (Hub and Spoke)
- Deploy identity resources with custom settings
- Deploy management resources with custom settings
- Expand built-in archetype definitions
- Create custom policies, initiatives and assignments
- Override module role assignments
- Control policy enforcement mode
- Policy assignments with user assigned managed identities
- Level 400
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Troubleshooting
- Contributing