-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 64
shapes.scad
Common useful shapes and structured objects. To use, add the following lines to the beginning of your file:
include <BOSL/constants.scad>
use <BOSL/shapes.scad>
Description: Creates a cube or cuboid object, with optional chamfering or filleting/rounding.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
The size of the cube. |
chamfer |
Size of chamfer, inset from sides. Default: No chamferring. |
fillet |
Radius of fillet for edge rounding. Default: No filleting. |
edges |
Edges to chamfer/fillet. Use EDGE constants from constants.scad. Default: EDGES_ALL
|
trimcorners |
If true, rounds or chamfers corners where three chamferred/filleted edges meet. Default: true
|
p1 |
Align the cuboid's corner at p1, if given. Forces align=V_UP+V_BACK+V_RIGHT. |
p2 |
If given with p1, defines the cornerpoints of the cuboid. |
align |
The side of the origin to align to. Use V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER
|
center |
If given, overrides align. A true value sets align=V_CENTER, false sets align=V_UP+V_BACK+V_RIGHT. |
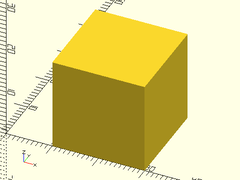
Example 1: Simple regular cube.
cuboid(40);
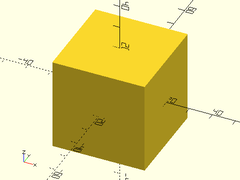
Example 2: Cube with minimum cornerpoint given.
cuboid(20, p1=[10,0,0]);
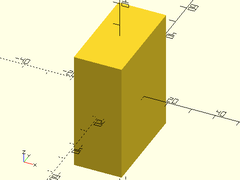
Example 3: Rectangular cube, with given X, Y, and Z sizes.
cuboid([20,40,50]);
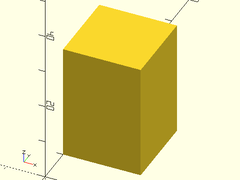
Example 4: Rectangular cube defined by opposing cornerpoints.
cuboid(p1=[0,10,0], p2=[20,30,30]);
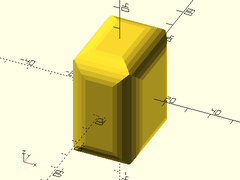
Example 5: Rectangular cube with chamferred edges and corners.
cuboid([30,40,50], chamfer=5);
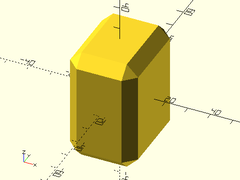
Example 6: Rectangular cube with chamferred edges, without trimmed corners.
cuboid([30,40,50], chamfer=5, trimcorners=false);
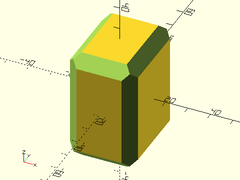
Example 7: Rectangular cube with rounded edges and corners.
cuboid([30,40,50], fillet=10);
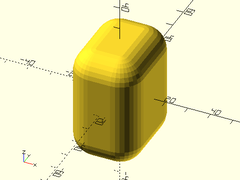
Example 8: Rectangular cube with rounded edges, without trimmed corners.
cuboid([30,40,50], fillet=10, trimcorners=false);
Example 9: Rectangular cube with only some edges chamferred.
cuboid([30,40,50], chamfer=5, edges=EDGE_TOP_FR+EDGE_TOP_RT+EDGE_FR_RT, $fn=24);
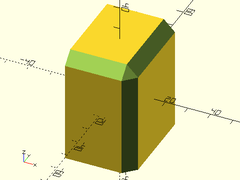
Example 10: Rectangular cube with only some edges rounded.
cuboid([30,40,50], fillet=5, edges=EDGE_TOP_FR+EDGE_TOP_RT+EDGE_FR_RT, $fn=24);
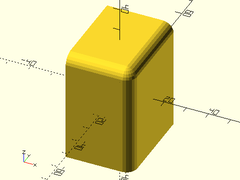
Description: Creates a cube that spans the X, Y, and Z ranges given.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
xspan |
[min, max] X axis range. |
yspan |
[min, max] Y axis range. |
zspan |
[min, max] Z axis range. |
Example:
span_cube([0,15], [5,10], [0, 10]);
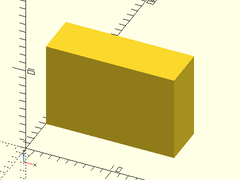
Usage:
- leftcube(size);
Description: Makes a cube that is aligned on the left side of the origin.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
The size of the cube to make. |
Example:
leftcube([20,30,40]);
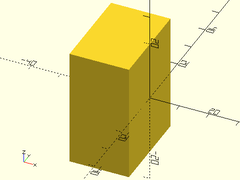
Usage:
- rightcube(size);
Description: Makes a cube that is aligned on the right side of the origin.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
The size of the cube to make. |
Example:
rightcube([20,30,40]);
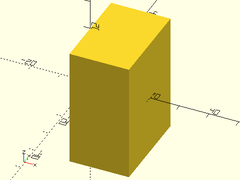
Usage:
- fwdcube(size);
Description: Makes a cube that is aligned on the front side of the origin.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
The size of the cube to make. |
Example:
fwdcube([20,30,40]);
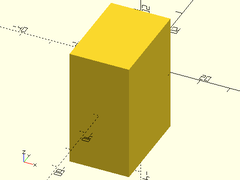
Usage:
- backcube(size);
Description: Makes a cube that is aligned on the front side of the origin.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
The size of the cube to make. |
Example:
backcube([20,30,40]);
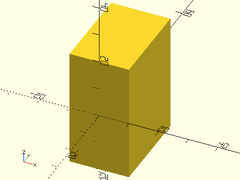
Usage:
- downcube(size);
Description: Makes a cube that is aligned on the bottom side of the origin.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
The size of the cube to make. |
Example:
downcube([20,30,40]);
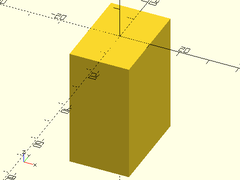
Usage:
- upcube(size);
Description: Makes a cube that is aligned on the top side of the origin.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
The size of the cube to make. |
Example:
upcube([20,30,40]);
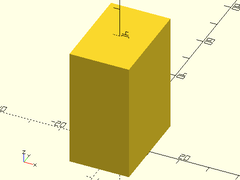
Usage:
- prismoid(size1, size2, h, [shift], [orient], [align|center]);
Description: Creates a rectangular prismoid shape.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size1 |
[width, length] of the axis-negative end of the prism. |
size2 |
[width, length] of the axis-positive end of the prism. |
h |
Height of the prism. |
shift |
[x, y] amount to shift the center of the top with respect to the center of the bottom. |
orient |
Orientation of the prismoid. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the prismoid by the axis-negative (size1) end. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ALIGN_POS. |
center |
If given, overrides align. A true value sets align=V_CENTER, false sets align=ALIGN_POS. |
Example 1: Rectangular Pyramid
prismoid(size1=[40,40], size2=[0,0], h=20);
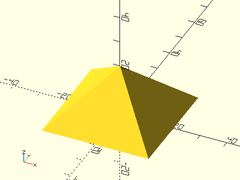
Example 2: Prism
prismoid(size1=[40,40], size2=[0,40], h=20);
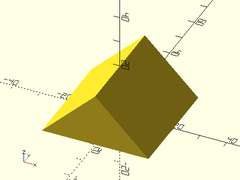
Example 3: Truncated Pyramid
prismoid(size1=[35,50], size2=[20,30], h=20);
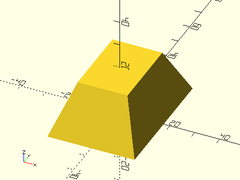
Example 4: Wedge
prismoid(size1=[60,35], size2=[30,0], h=30);
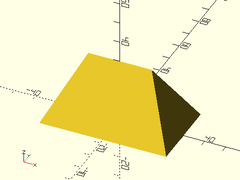
Example 5: Truncated Tetrahedron
prismoid(size1=[10,40], size2=[40,10], h=40);
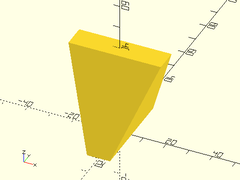
Example 6: Inverted Truncated Pyramid
prismoid(size1=[15,5], size2=[30,20], h=20);
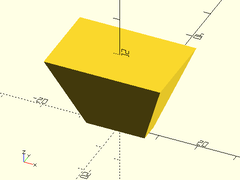
Example 7: Right Prism
prismoid(size1=[30,60], size2=[0,60], shift=[-15,0], h=30);
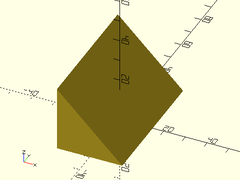
Example 8: Shifting/Skewing
prismoid(size1=[50,30], size2=[20,20], h=20, shift=[15,5]);
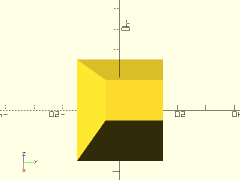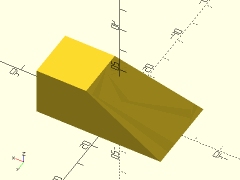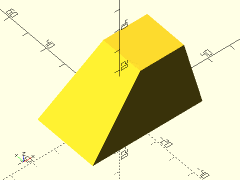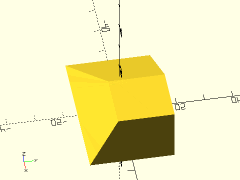
Description: Creates a rectangular prismoid shape with rounded vertical edges.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size1 |
[width, length] of the bottom of the prism. |
size2 |
[width, length] of the top of the prism. |
h |
Height of the prism. |
r |
radius of vertical edge fillets. |
r1 |
radius of vertical edge fillets at bottom. |
r2 |
radius of vertical edge fillets at top. |
shift |
[x, y] amount to shift the center of the top with respect to the center of the bottom. |
orient |
Orientation of the prismoid. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the prismoid by the axis-negative (size1) end. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_UP. |
center |
vertically center the prism. Overrides align. |
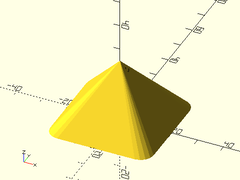
Example 1: Rounded Pyramid
rounded_prismoid(size1=[40,40], size2=[0,0], h=25, r=5);
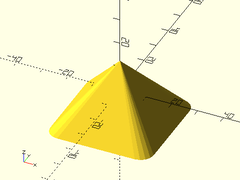
Example 2: Centered Rounded Pyramid
rounded_prismoid(size1=[40,40], size2=[0,0], h=25, r=5, center=true);
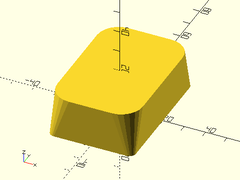
Example 3: Disparate Top and Bottom Radii
rounded_prismoid(size1=[40,60], size2=[40,60], h=20, r1=3, r2=10, $fn=24);
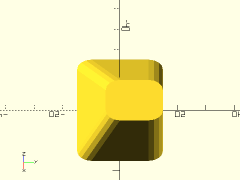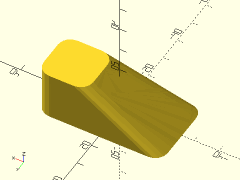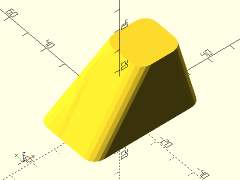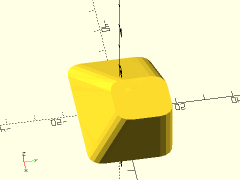
Example 4: Shifting/Skewing
rounded_prismoid(size1=[50,30], size2=[20,20], h=20, shift=[15,5], r=5);
Usage:
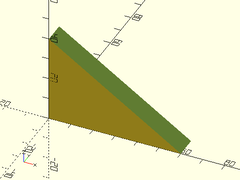
- right_triangle(size, [orient], [align|center]);
Description: Creates a 3D right triangular prism.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
[width, thickness, height] |
orient |
The axis to place the hypotenuse along. Only accepts ORIENT_X, ORIENT_Y, or ORIENT_Z from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
The side of the origin to align to. Use V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_UP+V_BACK+V_RIGHT. |
center |
If given, overrides align. A true value sets align=V_CENTER, false sets align=V_UP+V_BACK+V_RIGHT. |
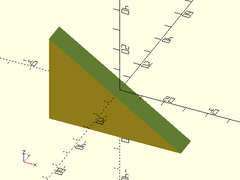
Example 1: Centered
right_triangle([60, 10, 40], center=true);
Example 2: Non-Centered
right_triangle([60, 10, 40]);
Normal Cylinders:
- cyl(l|h, r|d, [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
- cyl(l|h, r1|d1, r2/d2, [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
Chamferred Cylinders:
- cyl(l|h, r|d, chamfer, [chamfang], [from_end], [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
- cyl(l|h, r|d, chamfer1, [chamfang1], [from_end], [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
- cyl(l|h, r|d, chamfer2, [chamfang2], [from_end], [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
- cyl(l|h, r|d, chamfer1, chamfer2, [chamfang1], [chamfang2], [from_end], [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
Rounded/Filleted Cylinders:
- cyl(l|h, r|d, fillet, [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
- cyl(l|h, r|d, fillet1, [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
- cyl(l|h, r|d, fillet2, [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
- cyl(l|h, r|d, fillet1, fillet2, [circum], [realign], [orient], [align], [center]);
Description:
Creates cylinders in various alignments and orientations,
with optional fillets and chamfers. You can use r and l
interchangably, and all variants allow specifying size
by either r|d, or r1|d1 and r2|d2.
Note that that chamfers and fillets cannot cross the
midpoint of the cylinder's length.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
l / h
|
Length of cylinder along oriented axis. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
Radius of cylinder. |
r1 |
Radius of the negative (X-, Y-, Z-) end of cylinder. |
r2 |
Radius of the positive (X+, Y+, Z+) end of cylinder. |
d |
Diameter of cylinder. |
d1 |
Diameter of the negative (X-, Y-, Z-) end of cylinder. |
d2 |
Diameter of the positive (X+, Y+, Z+) end of cylinder. |
circum |
If true, cylinder should circumscribe the circle of the given size. Otherwise inscribes. Default: false
|
chamfer |
The size of the chamfers on the ends of the cylinder. Default: none. |
chamfer1 |
The size of the chamfer on the axis-negative end of the cylinder. Default: none. |
chamfer2 |
The size of the chamfer on the axis-positive end of the cylinder. Default: none. |
chamfang |
The angle in degrees of the chamfers on the ends of the cylinder. |
chamfang1 |
The angle in degrees of the chamfer on the axis-negative end of the cylinder. |
chamfang2 |
The angle in degrees of the chamfer on the axis-positive end of the cylinder. |
from_end |
If true, chamfer is measured from the end of the cylinder, instead of inset from the edge. Default: false. |
fillet |
The radius of the fillets on the ends of the cylinder. Default: none. |
fillet1 |
The radius of the fillet on the axis-negative end of the cylinder. |
fillet2 |
The radius of the fillet on the axis-positive end of the cylinder. |
realign |
If true, rotate the cylinder by half the angle of one face. |
orient |
Orientation of the cylinder. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: vertical. |
align |
Alignment of the cylinder. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: centered. |
center |
If given, overrides align. A true value sets align=V_CENTER, false sets align=ALIGN_POS. |
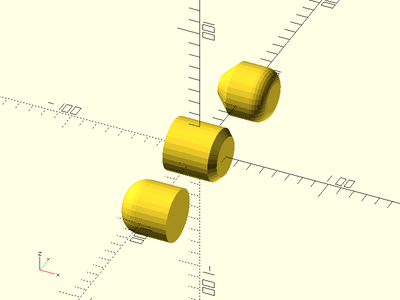
Example 1: By Radius
xdistribute(30) {
cyl(l=40, r=10);
cyl(l=40, r1=10, r2=5);
}
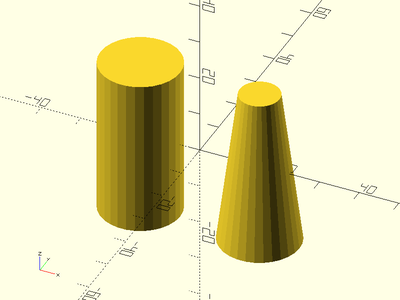
Example 2: By Diameter
xdistribute(30) {
cyl(l=40, d=25);
cyl(l=40, d1=25, d2=10);
}
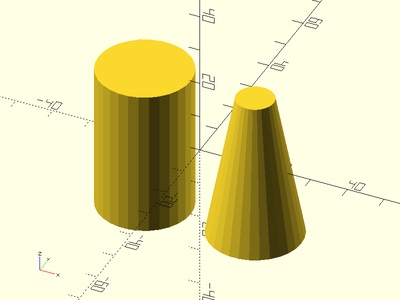
Example 3: Chamferring
xdistribute(60) {
// Shown Left to right.
cyl(l=40, d=40, chamfer=7); // Default chamfang=45
cyl(l=40, d=40, chamfer=7, chamfang=30, from_end=false);
cyl(l=40, d=40, chamfer=7, chamfang=30, from_end=true);
}
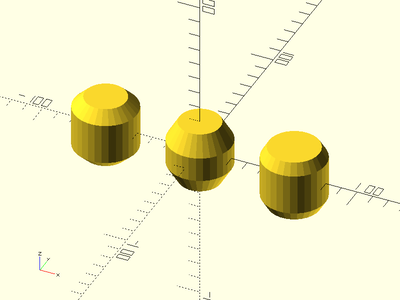
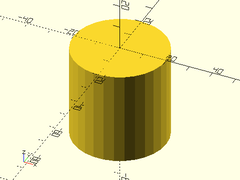
Example 4: Rounding/Filleting
cyl(l=40, d=40, fillet=10);
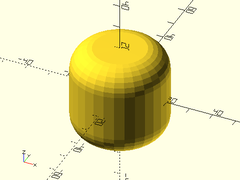
Example 5: Heterogenous Chamfers and Fillets
ydistribute(80) {
// Shown Front to Back.
cyl(l=40, d=40, fillet1=15, orient=ORIENT_X);
cyl(l=40, d=40, chamfer2=5, orient=ORIENT_X);
cyl(l=40, d=40, chamfer1=12, fillet2=10, orient=ORIENT_X);
}
Example 6: Putting it all together
cyl(l=40, d1=25, d2=15, chamfer1=10, chamfang1=30, from_end=true, fillet2=5);
Usage:
- downcyl(l|h, r|d);
- downcyl(l|h, r1|d1, r2|d2);
Description: Creates a cylinder aligned below the origin.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
l / h
|
Length of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
Radius of cylinder. |
r1 |
Bottom radius of cylinder. |
r2 |
Top radius of cylinder. |
d |
Diameter of cylinder. (use instead of r) |
d1 |
Bottom diameter of cylinder. |
d2 |
Top diameter of cylinder. |
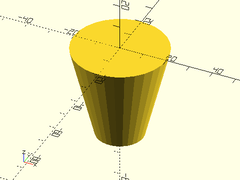
Example 1: Cylinder
downcyl(r=20, h=40);
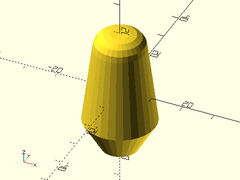
Example 2: Cone
downcyl(r1=10, r2=20, h=40);
Usage:
- xcyl(l|h, r|d, [align|center]);
- xcyl(l|h, r1|d1, r2|d2, [align|center]);
Description: Creates a cylinder oriented along the X axis.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
l / h
|
Length of cylinder along oriented axis. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
Radius of cylinder. |
r1 |
Optional radius of left (X-) end of cylinder. |
r2 |
Optional radius of right (X+) end of cylinder. |
d |
Optional diameter of cylinder. (use instead of r) |
d1 |
Optional diameter of left (X-) end of cylinder. |
d2 |
Optional diameter of right (X+) end of cylinder. |
align |
The side of the origin to align to. Use V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER
|
center |
If given, overrides align. A true value sets align=V_CENTER, false sets align=ALIGN_POS. |
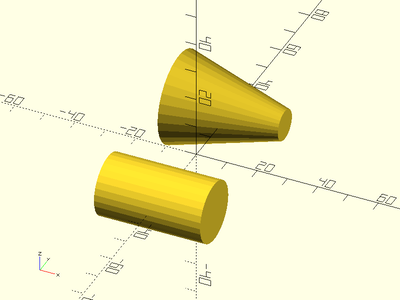
Example 1: By Radius
ydistribute(50) {
xcyl(l=35, r=10);
xcyl(l=35, r1=15, r2=5);
}
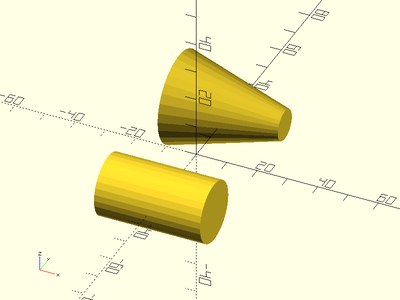
Example 2: By Diameter
ydistribute(50) {
xcyl(l=35, d=20);
xcyl(l=35, d1=30, d2=10);
}
Usage:
- ycyl(l|h, r|d, [align|center]);
- ycyl(l|h, r1|d1, r2|d2, [align|center]);
Description: Creates a cylinder oriented along the Y axis.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
l / h
|
Length of cylinder along oriented axis. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
Radius of cylinder. |
r1 |
Radius of front (Y-) end of cone. |
r2 |
Radius of back (Y+) end of one. |
d |
Diameter of cylinder. |
d1 |
Diameter of front (Y-) end of one. |
d2 |
Diameter of back (Y+) end of one. |
align |
The side of the origin to align to. Use V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER
|
center |
Overrides align if given. If true, align=V_CENTER, if false, align=ALIGN_POS. |
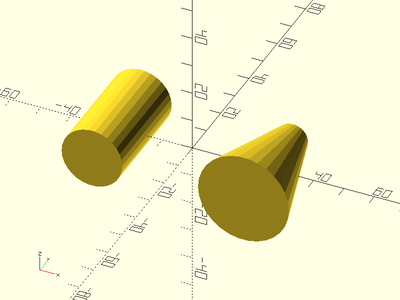
Example 1: By Radius
xdistribute(50) {
ycyl(l=35, r=10);
ycyl(l=35, r1=15, r2=5);
}
Example 2: By Diameter
xdistribute(50) {
ycyl(l=35, d=20);
ycyl(l=35, d1=30, d2=10);
}
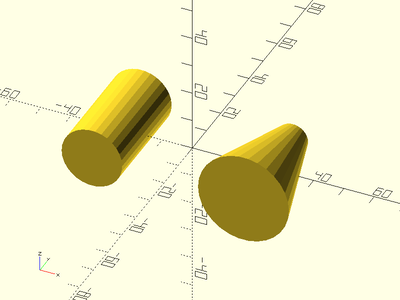
Usage:
- zcyl(l|h, r|d, [align|center]);
- zcyl(l|h, r1|d1, r2|d2, [align|center]);
Description: Creates a cylinder oriented along the Z axis.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
l / h
|
Length of cylinder along oriented axis. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
Radius of cylinder. |
r1 |
Radius of front (Y-) end of cone. |
r2 |
Radius of back (Y+) end of one. |
d |
Diameter of cylinder. |
d1 |
Diameter of front (Y-) end of one. |
d2 |
Diameter of back (Y+) end of one. |
align |
The side of the origin to align to. Use V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER
|
center |
Overrides align if given. If true, align=V_CENTER, if false, align=ALIGN_POS. |
Example 1: By Radius
xdistribute(50) {
zcyl(l=35, r=10);
zcyl(l=35, r1=15, r2=5);
}
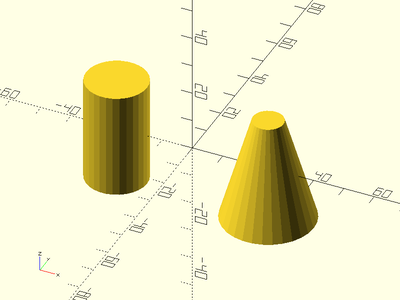
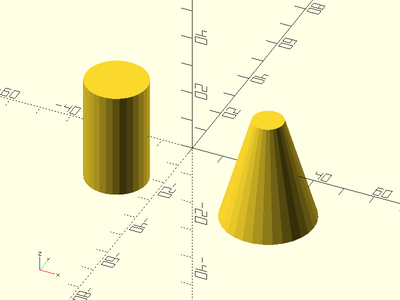
Example 2: By Diameter
xdistribute(50) {
zcyl(l=35, d=20);
zcyl(l=35, d1=30, d2=10);
}
Usage:
- tube(h, ir|id, wall, [realign], [orient], [align]);
- tube(h, or|od, wall, [realign], [orient], [align]);
- tube(h, ir|id, or|od, [realign], [orient], [align]);
- tube(h, ir1|id1, ir2|id2, wall, [realign], [orient], [align]);
- tube(h, or1|od1, or2|od2, wall, [realign], [orient], [align]);
- tube(h, ir1|id1, ir2|id2, or1|od1, or2|od2, [realign], [orient], [align]);
Description: Makes a hollow tube with the given outer size and wall thickness.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of tube. (Default: 1) |
or |
Outer radius of tube. |
or1 |
Outer radius of bottom of tube. (Default: value of r) |
or2 |
Outer radius of top of tube. (Default: value of r) |
od |
Outer diameter of tube. |
od1 |
Outer diameter of bottom of tube. |
od2 |
Outer diameter of top of tube. |
wall |
horizontal thickness of tube wall. (Default 0.5) |
ir |
Inner radius of tube. |
ir1 |
Inner radius of bottom of tube. |
ir2 |
Inner radius of top of tube. |
id |
Inner diameter of tube. |
id1 |
Inner diameter of bottom of tube. |
id2 |
Inner diameter of top of tube. |
realign |
If true, rotate the tube by half the angle of one face. |
orient |
Orientation of the tube. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: vertical. |
align |
Alignment of the tube. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ALIGN_POS. |
center |
Overrides align if given. If true, align=V_CENTER, if false, align=ALIGN_POS. |
Example 1: These all Produce the Same Tube
tube(h=30, or=40, wall=5);
tube(h=30, ir=35, wall=5);
tube(h=30, or=40, ir=35);
tube(h=30, od=80, id=70);
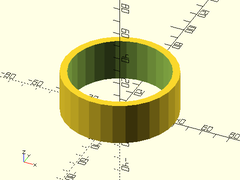
Example 2: These all Produce the Same Conical Tube
tube(h=30, or1=40, or2=25, wall=5);
tube(h=30, ir1=35, or2=20, wall=5);
tube(h=30, or1=40, or2=25, ir1=35, ir2=20);
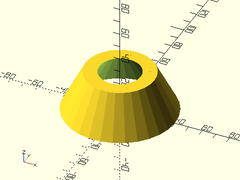
Example 3: Circular Wedge
tube(h=30, or1=40, or2=30, ir1=20, ir2=30);
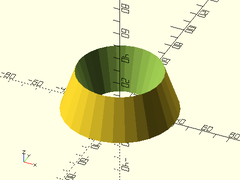
Usage:
- torus(r|d, r2|d2, [orient], [align]);
- torus(or|od, ir|id, [orient], [align]);
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
r |
major radius of torus ring. (use with of 'r2', or 'd2') |
r2 |
minor radius of torus ring. (use with of 'r', or 'd') |
d |
major diameter of torus ring. (use with of 'r2', or 'd2') |
d2 |
minor diameter of torus ring. (use with of 'r', or 'd') |
or |
outer radius of the torus. (use with 'ir', or 'id') |
ir |
inside radius of the torus. (use with 'or', or 'od') |
od |
outer diameter of the torus. (use with 'ir' or 'id') |
id |
inside diameter of the torus. (use with 'or' or 'od') |
orient |
Orientation of the torus. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the torus. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
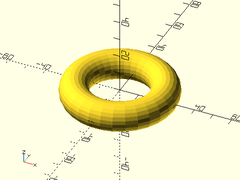
Example:
// These all produce the same torus.
torus(r=22.5, r2=7.5);
torus(d=45, d2=15);
torus(or=30, ir=15);
torus(od=60, id=30);
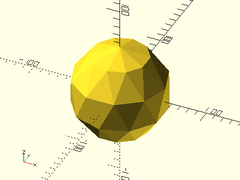
Usage:
- staggered_sphere(r|d, [circum])
Description:
An alternate construction to the standard sphere() built-in, with different triangulation.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
r |
Radius of the sphere. |
d |
Diameter of the sphere. |
circum |
If true, circumscribes the perfect sphere of the given size. |
Example:
staggered_sphere(d=100, circum=true, $fn=10);
Usage:
- teardrop2d(r|d, [ang], [cap_h]);
Description: Makes a 2D teardrop shape. Useful for extruding into 3D printable holes.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
r |
radius of circular part of teardrop. (Default: 1) |
d |
diameter of spherical portion of bottom. (Use instead of r) |
ang |
angle of hat walls from the Y axis. (Default: 45 degrees) |
cap_h |
if given, height above center where the shape will be truncated. |
Example 1: Typical Shape
teardrop2d(r=30, ang=30);
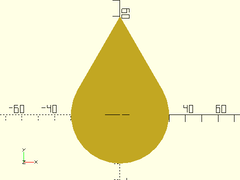
Example 2: Crop Cap
teardrop2d(r=30, ang=30, cap_h=40);
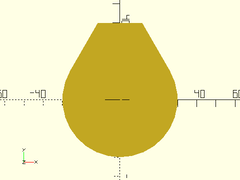
Example 3: Close Crop
teardrop2d(r=30, ang=30, cap_h=20);
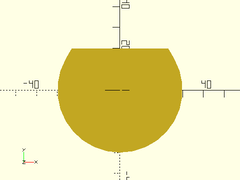
Usage:
- teardrop(r|d, l|h, [ang], [cap_h], [orient], [align])
Description: Makes a teardrop shape in the XZ plane. Useful for 3D printable holes.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
r |
Radius of circular part of teardrop. (Default: 1) |
d |
Diameter of circular portion of bottom. (Use instead of r) |
l |
Thickness of teardrop. (Default: 1) |
ang |
Angle of hat walls from the Z axis. (Default: 45 degrees) |
cap_h |
If given, height above center where the shape will be truncated. |
orient |
Orientation of the shape. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1: Typical Shape
teardrop(r=30, h=10, ang=30);
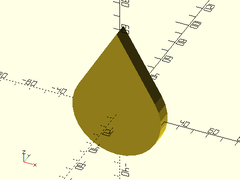
Example 2: Crop Cap
teardrop(r=30, h=10, ang=30, cap_h=40);
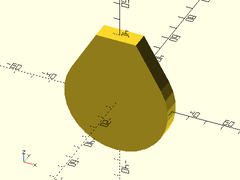
Example 3: Close Crop
teardrop(r=30, h=10, ang=30, cap_h=20);
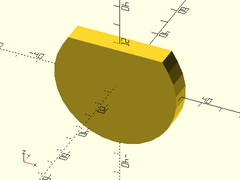
Usage:
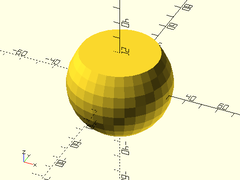
- onion(r|d, [maxang], [cap_h], [orient], [align]);
Description: Creates a sphere with a conical hat, to make a 3D teardrop.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
r |
radius of spherical portion of the bottom. (Default: 1) |
d |
diameter of spherical portion of bottom. |
cap_h |
height above sphere center to truncate teardrop shape. |
maxang |
angle of cone on top from vertical. |
orient |
Orientation of the shape. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
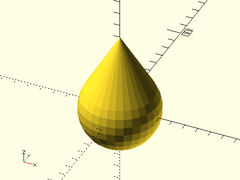
Example 1: Typical Shape
onion(r=30, maxang=30);
Example 2: Crop Cap
onion(r=30, maxang=30, cap_h=40);
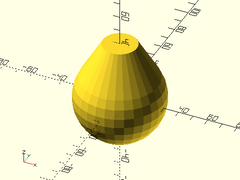
Example 3: Close Crop
onion(r=30, maxang=30, cap_h=20);
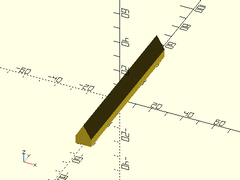
Usage:
- narrowing_strut(w, l, wall, [ang], [orient], [align]);
Description: Makes a rectangular strut with the top side narrowing in a triangle. The shape created may be likened to an extruded home plate from baseball. This is useful for constructing parts that minimize the need to support overhangs.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
w |
Width (thickness) of the strut. |
l |
Length of the strut. |
wall |
height of rectangular portion of the strut. |
ang |
angle that the trianglar side will converge at. |
orient |
Orientation of the length axis of the shape. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example:
narrowing_strut(w=10, l=100, wall=5, ang=30);
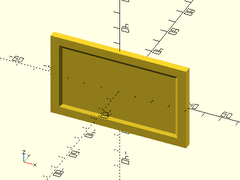
Usage:
- thinning_wall(h, l, thick, [ang], [strut], [wall], [orient], [align]);
Description: Makes a rectangular wall which thins to a smaller width in the center, with angled supports to prevent critical overhangs.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of wall. |
l |
length of wall. If given as a vector of two numbers, specifies bottom and top lengths, respectively. |
thick |
thickness of wall. |
ang |
maximum overhang angle of diagonal brace. |
strut |
the width of the diagonal brace. |
wall |
the thickness of the thinned portion of the wall. |
orient |
Orientation of the length axis of the wall. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_X. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1: Typical Shape
thinning_wall(h=50, l=80, thick=4);
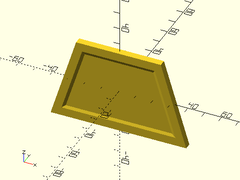
Example 2: Trapezoidal
thinning_wall(h=50, l=[80,50], thick=4);
Usage:
- braced_thinning_wall(h, l, thick, [ang], [strut], [wall], [orient], [align]);
Description: Makes a rectangular wall with cross-bracing, which thins to a smaller width in the center, with angled supports to prevent critical overhangs.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of wall. |
l |
length of wall. |
thick |
thickness of wall. |
ang |
maximum overhang angle of diagonal brace. |
strut |
the width of the diagonal brace. |
wall |
the thickness of the thinned portion of the wall. |
orient |
Orientation of the length axis of the wall. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example: Typical Shape
braced_thinning_wall(h=50, l=100, thick=5);
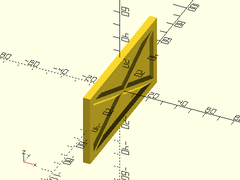
Usage:
- thinning_triangle(h, l, thick, [ang], [strut], [wall], [diagonly], [orient], [align|center]);
Description: Makes a triangular wall with thick edges, which thins to a smaller width in the center, with angled supports to prevent critical overhangs.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of wall. |
l |
length of wall. |
thick |
thickness of wall. |
ang |
maximum overhang angle of diagonal brace. |
strut |
the width of the diagonal brace. |
wall |
the thickness of the thinned portion of the wall. |
diagonly |
boolean, which denotes only the diagonal side (hypotenuse) should be thick. |
orient |
Orientation of the length axis of the shape. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
center |
If true, centers shape. If false, overrides align with V_UP+V_BACK. |
Example 1: Centered
thinning_triangle(h=50, l=80, thick=4, ang=30, strut=5, wall=2, center=true);
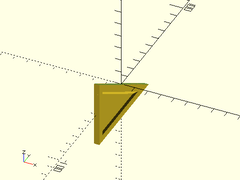
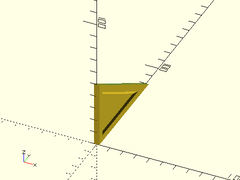
Example 2: All Braces
thinning_triangle(h=50, l=80, thick=4, ang=30, strut=5, wall=2, center=false);
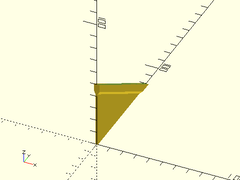
Example 3: Diagonal Brace Only
thinning_triangle(h=50, l=80, thick=4, ang=30, strut=5, wall=2, diagonly=true, center=false);
Usage:
- sparse_strut(h, l, thick, [strut], [maxang], [max_bridge], [orient], [align])
Description: Makes an open rectangular strut with X-shaped cross-bracing, designed to reduce the need for support material in 3D printing.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of strut wall. |
l |
length of strut wall. |
thick |
thickness of strut wall. |
maxang |
maximum overhang angle of cross-braces. |
max_bridge |
maximum bridging distance between cross-braces. |
strut |
the width of the cross-braces. |
orient |
Orientation of the length axis of the shape. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1: Typical Shape
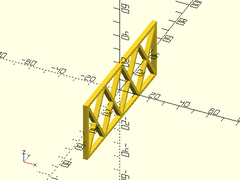
sparse_strut(h=40, l=100, thick=3);
Example 2: Thinner Strut
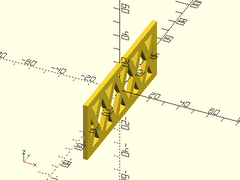
sparse_strut(h=40, l=100, thick=3, strut=2);
Example 3: Larger maxang
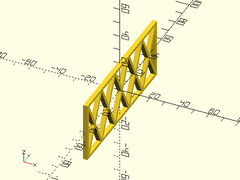
sparse_strut(h=40, l=100, thick=3, strut=2, maxang=45);
Example 4: Longer max_bridge
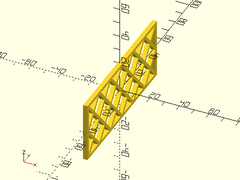
sparse_strut(h=40, l=100, thick=3, strut=2, maxang=45, max_bridge=30);
Usage:
- sparse_strut3d(h, w, l, [thick], [maxang], [max_bridge], [strut], [orient], [align]);
Description: Makes an open rectangular strut with X-shaped cross-bracing, designed to reduce the need for support material in 3D printing.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
Z size of strut. |
w |
X size of strut. |
l |
Y size of strut. |
thick |
thickness of strut walls. |
maxang |
maximum overhang angle of cross-braces. |
max_bridge |
maximum bridging distance between cross-braces. |
strut |
the width of the cross-braces. |
orient |
Orientation of the length axis of the shape. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
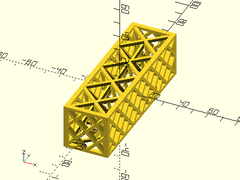
Example 1: Typical Shape
sparse_strut3d(h=30, w=30, l=100);
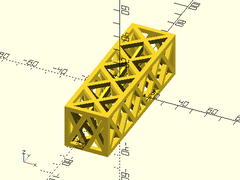
Example 2: Thinner strut
sparse_strut3d(h=30, w=30, l=100, strut=2);
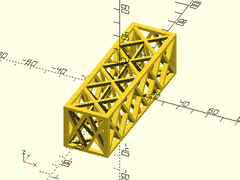
Example 3: Larger maxang
sparse_strut3d(h=30, w=30, l=100, strut=2, maxang=50);
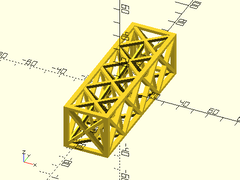
Example 4: Smaller max_bridge
sparse_strut3d(h=30, w=30, l=100, strut=2, maxang=50, max_bridge=20);
Usage:
- corrugated_wall(h, l, thick, [strut], [wall], [orient], [align]);
Description: Makes a corrugated wall which relieves contraction stress while still providing support strength. Designed with 3D printing in mind.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of strut wall. |
l |
length of strut wall. |
thick |
thickness of strut wall. |
strut |
the width of the cross-braces. |
wall |
thickness of corrugations. |
orient |
Orientation of the length axis of the shape. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Y. |
align |
Alignment of the shape. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
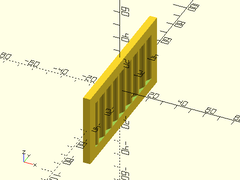
Example 1: Typical Shape
corrugated_wall(h=50, l=100);
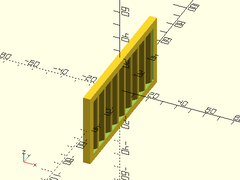
Example 2: Wider Strut
corrugated_wall(h=50, l=100, strut=8);
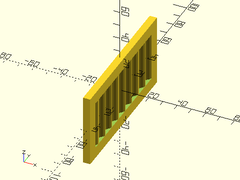
Example 3: Thicker Wall
corrugated_wall(h=50, l=100, strut=8, wall=3);
Description: Useful when you MUST pass a child to a module, but you want it to be nothing.
Description: Passes through the children passed to it, with no action at all. Useful while debugging when you want to replace a command.
Usage:
- pie_slice(ang, l|h, r|d, [orient], [align|center]);
- pie_slice(ang, l|h, r1|d1, r2|d2, [orient], [align|center]);
Description: Creates a pie slice shape.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
ang |
pie slice angle in degrees. |
h |
height of pie slice. |
r |
radius of pie slice. |
r1 |
bottom radius of pie slice. |
r2 |
top radius of pie slice. |
d |
diameter of pie slice. |
d1 |
bottom diameter of pie slice. |
d2 |
top diameter of pie slice. |
orient |
Orientation of the pie slice. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the pie slice. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
center |
If given, overrides align. A true value sets align=V_CENTER, false sets align=ALIGN_POS. |
Example 1: Cylindrical Pie Slice
pie_slice(ang=45, l=20, r=30);
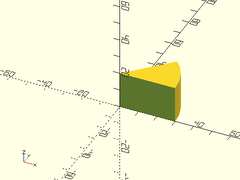
Example 2: Conical Pie Slice
pie_slice(ang=60, l=20, d1=50, d2=70);
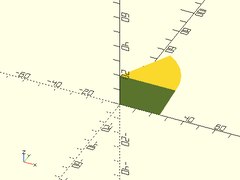
Usage:
- interior_fillet(l, r, [ang], [overlap], [orient], [align]);
Description: Creates a shape that can be unioned into a concave joint between two faces, to fillet them. Center this part along the concave edge to be chamferred and union it in.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
l |
length of edge to fillet. |
r |
radius of fillet. |
ang |
angle between faces to fillet. |
overlap |
overlap size for unioning with faces. |
orient |
Orientation of the fillet. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_X. |
align |
Alignment of the fillet. Use the V_ or ALIGN_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1:
union() {
translate([0,2,-4]) upcube([20, 4, 24]);
translate([0,-10,-4]) upcube([20, 20, 4]);
color("green") interior_fillet(l=20, r=10, orient=ORIENT_XNEG);
}
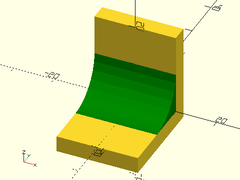
Example 2:
interior_fillet(l=40, r=10, orient=ORIENT_Y_90);
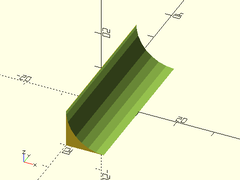
Usage:
- slot(h, l, r|d, [orient], [align|center]);
- slot(h, p1, p2, r|d, [orient], [align|center]);
- slot(h, l, r1|d1, r2|d2, [orient], [align|center]);
- slot(h, p1, p2, r1|d1, r2|d2, [orient], [align|center]);
Description: Makes a linear slot with rounded ends, appropriate for bolts to slide along.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
p1 |
center of starting circle of slot. |
p2 |
center of ending circle of slot. |
l |
distance between center points of starting and ending circle. |
h |
height of slot shape. (default: 10) |
r |
radius of slot circle. (default: 5) |
r1 |
bottom radius of slot cone. |
r2 |
top radius of slot cone. |
d |
diameter of slot circle. |
d1 |
bottom diameter of slot cone. |
d2 |
top diameter of slot cone. |
Example 1: Between Two Points
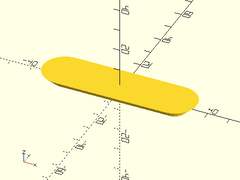
slot([0,0,0], [50,50,0], r1=5, r2=10, h=5);
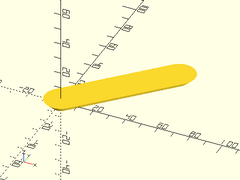
Example 2: By Length
slot(l=50, r1=5, r2=10, h=5);
Usage:
- arced_slot(h, r|d, sr|sd, [sa], [ea], [orient], [align|center], [$fn2]);
- arced_slot(h, r|d, sr1|sd1, sr2|sd2, [sa], [ea], [orient], [align|center], [$fn2]);
Description: Makes an arced slot, appropriate for bolts to slide along.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
cp |
centerpoint of slot arc. (default: [0, 0, 0]) |
h |
height of slot arc shape. (default: 1.0) |
r |
radius of slot arc. (default: 0.5) |
d |
diameter of slot arc. (default: 1.0) |
sr |
radius of slot channel. (default: 0.5) |
sd |
diameter of slot channel. (default: 0.5) |
sr1 |
bottom radius of slot channel cone. (use instead of sr) |
sr2 |
top radius of slot channel cone. (use instead of sr) |
sd1 |
bottom diameter of slot channel cone. (use instead of sd) |
sd2 |
top diameter of slot channel cone. (use instead of sd) |
sa |
starting angle. (Default: 0.0) |
ea |
ending angle. (Default: 90.0) |
orient |
Orientation of the arced slot. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the arced slot. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
center |
If true, centers vertically. If false, drops flush with XY plane. Overrides align. |
$fn2 |
The $fn value to use on the small round endcaps. The major arcs are still based on $fn. Default: $fn |
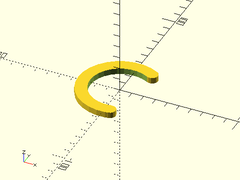
Example 1: Typical Arced Slot
arced_slot(d=60, h=5, sd=10, sa=60, ea=280);
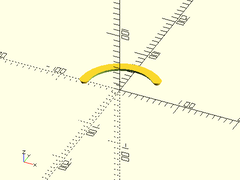
Example 2: Conical Arced Slot
arced_slot(r=60, h=5, sd1=10, sd2=15, sa=45, ea=180);
DEPRECATED, use cuboid(p1,p2) instead.
Usage:
- cube2pt(p1,p2)
Description: Creates a cube between two points.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
p1 |
Coordinate point of one cube corner. |
p2 |
Coordinate point of opposite cube corner. |
DEPRECATED, use cuboid(..., align) instead.
Description:
Makes a cube that is offset along the given vector by half the cube's size.
For example, if v=[-1,1,0], the cube's front right edge will be centered at the origin.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
size of cube. |
v |
vector to offset along. |
DEPRECATED, use cuboid(..., chamfer, edges, trimcorners) instead.
Description: Makes a cube with chamfered edges.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
Size of cube [X,Y,Z]. (Default: [1,1,1]) |
chamfer |
Chamfer inset along axis. (Default: 0.25) |
chamfaxes |
Array [X,Y,Z] of boolean values to specify which axis edges should be chamfered. |
chamfcorners |
Boolean to specify if corners should be flat chamferred. |
DEPRECATED, use cuboid(..., fillet, edges) instead.
Description:
Makes a cube with rounded (filletted) vertical edges. The r size will be
limited to a maximum of half the length of the shortest XY side.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
Size of cube [X,Y,Z]. (Default: [1,1,1]) |
r |
Radius of edge/corner rounding. (Default: 0.25) |
center |
If true, object will be centered. If false, sits on top of XY plane. |
DEPRECATED, use cuboid(..., fillet) instead.
Description:
Makes a cube with rounded (filletted) edges and corners. The r size will be
limited to a maximum of half the length of the shortest cube side.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size |
Size of cube [X,Y,Z]. (Default: [1,1,1]) |
r |
Radius of edge/corner rounding. (Default: 0.25) |
center |
If true, object will be centered. If false, sits on top of XY plane. |
DEPRECATED, use prismoid() instead.
Usage:
- trapezoid(size1, size2, h, [shift], [orient], [align|center]);
Description: Creates a rectangular prismoid shape.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
size1 |
[width, length] of the axis-negative end of the prism. |
size2 |
[width, length] of the axis-positive end of the prism. |
h |
Height of the prism. |
shift |
[x, y] amount to shift the center of the top with respect to the center of the bottom. |
orient |
Orientation of the prismoid. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the prismoid by the axis-negative (size1) end. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_UP
|
center |
If given, overrides align. A true value sets align=V_CENTER, false sets align=V_UP. |
DEPRECATED, use cyl(, r2=0, $fn=N) instead.
Usage:
- pyramid(n, h, l|r|d, [circum]);
Description: Creates a pyramidal prism with a given number of sides.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
n |
number of pyramid sides. |
h |
height of the pyramid. |
l |
length of one side of the pyramid. (optional) |
r |
radius of the base of the pyramid. (optional) |
d |
diameter of the base of the pyramid. (optional) |
circum |
base circumscribes the circle of the given radius or diam. |
DEPRECATED, use cyl(..., $fn=N) instead.
Usage:
- prism(n, h, l|r|d, [circum]);
Description: Creates a vertical prism with a given number of sides.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
n |
number of sides. |
h |
height of the prism. |
l |
length of one side of the prism. (optional) |
r |
radius of the prism. (optional) |
d |
diameter of the prism. (optional) |
circum |
prism circumscribes the circle of the given radius or diam. |
DEPRECATED, use cyl(..., chamfer) instead.
Usage:
- chamferred_cylinder(h, r|d, chamfer|chamfedge, [top], [bottom], [center])
Description: Creates a cylinder with chamferred (bevelled) edges.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
radius of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
d |
diameter of cylinder. (use instead of r) |
chamfer |
radial inset of the edge chamfer. (Default: 0.25) |
chamfedge |
length of the chamfer edge. (Use instead of chamfer) |
top |
boolean. If true, chamfer the top edges. (Default: True) |
bottom |
boolean. If true, chamfer the bottom edges. (Default: True) |
center |
boolean. If true, cylinder is centered. (Default: false) |
DEPRECATED, use cyl(..., chamfer) instead.
Usage:
- chamf_cyl(h, r|d, chamfer|chamfedge, [top], [bottom], [center])
Description:
Creates a cylinder with chamferred (bevelled) edges. Basically a shortcut of chamferred_cylinder()
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
radius of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
d |
diameter of cylinder. (use instead of r) |
chamfer |
radial inset of the edge chamfer. (Default: 0.25) |
chamfedge |
length of the chamfer edge. (Use instead of chamfer) |
top |
boolean. If true, chamfer the top edges. (Default: True) |
bottom |
boolean. If true, chamfer the bottom edges. (Default: True) |
center |
boolean. If true, cylinder is centered. (Default: false) |
DEPRECATED, use cyl(..., fillet) instead.
Usage:
- filleted_cylinder(h, r|d, fillet, [center]);
Description: Creates a cylinder with filletted (rounded) ends.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
radius of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
d |
diameter of cylinder. (Use instead of r) |
fillet |
radius of the edge filleting. (Default: 0.25) |
center |
boolean. If true, cylinder is centered. (Default: false) |
DEPRECATED, use cyl(..., fillet) instead.
Usage:
- rcylinder(h, r|d, fillet, [center]);
Description:
Creates a cylinder with filletted (rounded) ends.
Basically a shortcut for filleted_cylinder().
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
r |
radius of cylinder. (Default: 1.0) |
d |
diameter of cylinder. (Use instead of r) |
fillet |
radius of the edge filleting. (Default: 0.25) |
center |
boolean. If true, cylinder is centered. (Default: false) |
DEPRECATED, use thinning_triangle(..., diagonly=true) instead.
Usage:
- thinning_brace(h, l, thick, [ang], [strut], [wall], [center])
Description: Makes a triangular wall which thins to a smaller width in the center, with angled supports to prevent critical overhangs. Basically an alias of thinning_triangle(), with diagonly=true.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
h |
height of wall. |
l |
length of wall. |
thick |
thickness of wall. |
ang |
maximum overhang angle of diagonal brace. |
strut |
the width of the diagonal brace. |
wall |
the thickness of the thinned portion of the wall. |